CHAPTER 2-LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 INTRODUCTION
In this chapter I have discussed and critically analyzed the literature related to competitive dimensions & advantages, which are crucial in modern economic environment. The effective strategies of IRL to attain competitive advantage have also been discussed here. Techno-economic parameters, cost effectiveness, human resource management issues, Research & Development, environment management, public relations, cost competitiveness, quality competitiveness, all these issues in regard to Refractory sector in India have been discussed in length. This section also discusses the policies of marketing and strategic planning as well as the demand for steel and its relevance to national economy.
2.2 COMPETITIVE DIMENSIONS & ADVANTAGES ARE CRUCIAL IN MODERN ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT
Given the choices that customers face today, how do they decide which product or service to buy? Different customers are attracted by different attributes. Some customers are primarily interested in the cost of a product or service, and correspondingly some companies attempt to position themselves to offer the lowest price. The major competitive dimensions that form the competitive position of a company include the following:
Cost – “Make it cheap” Within every industry, there is usually a segment of the market that buys solely on the basis of low cost. To successfully compete in this niche, a firm must be the low cost producer, but even doing this does not always guarantee profitability and success. (Harvard Business Review, 1996)
Product quality and reliability – “Make it good”. Quality can be divided into two categories: product quality and process quality. The level of quality in a product’s design will vary with the market segment at which it is aimed. Obviously, a child’s first two-wheeled bicycle is of significantly different quality than the bicycle of a world class cyclist. The goal in establishing the proper level of product quality is to focus on the requirements of the customer. Over-designed products with too much quality will be viewed as prohibitively expensive. Under-designed products, on the other hand, will lose customers to products that cost a little more but are perceived by the customers as offering greater value. (Harvard Business Review, 1996)
Process quality is critical because it relates directly to the reliability of the product. Regardless of whether the product is a child’s first two wheeler or a bicycle for an international cyclist, customers want products without defects. Thus, the goal of process quality is to produce error free products.
Delivery speed—“Make it fast.” In some markets, a company’s ability to delivery more quickly than its competitors may be critical. Seeing a need for speedy, reliable overnight delivery, FEDEX became a $15 billion company and the world’s large expedited delivery service. (Harvard Business Review, 1996)-Nov-Dec
Delivery reliability—“Deliver it when promised.” This dimension relates to the ability of the firm to supply the product or service on or before a promised delivery due date. For an automobile manufacturer it is very important that their supplier of tires provide the needed quantity and types for each day’s car production.
Coping with changes in demand – “Change its volume.” In many markets, a company’s ability to respond to increases and a decrease in demand is an important factor in its ability to compete. It is well known that a company with increasing demand can do little wrong. When demand is strong and increasing, costs are continuously reduced due to economics of scale, and investments in new technologies can be easily justified. But scaling back when demand decreases may require many difficult decisions relating to laying off employees and related reductions in assets. The ability to effectively deal with dynamic market demand over the loan term is an essential element of operations strategies.
Flexibility and new product introduction speed—“Change it”. Flexibility, from a strategic perspective refers to the ability of a company to offer a wide variety of products to its customers. An important element of this ability to offer different products is the time required for a company to develop a new product and to convert its processes to offer the new product. (Harvard Business Review, 1996)
2.3 EFFECTIVE STRATEGIES OF IRL TO ATTAIN COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE *
* Global marketing strategies by jean-pierre jeannet and H.david Hennessey PP: 583
India’s competitive advantage in Industrial Sector especially for Refractory products is emerging rapidly in the global markets other than its traditional setors like textiles, agricultural products, gems and Jewellery. However to sustain competitive advantage for moving steadily on the globalization path, the following steps are called for:
Adopting existing best industrial practices all over the globe and applying them efficiently according to Indian conditions will strengthen the effects of underlying success factors of India viz., cheaper labor rates and availability of potent technical workforce.
Industries which are low in skill and technological components and high on labor contents, natural resources or raw materials must strive to produce at lowest possible costs.
Sustained and cumulative investments in machines, development of industrial excellence and knowledge resources, use of information and communication technology and continuous process improvement will help the firm to sustain the competitive edge longer.
Creation of new advantages and continuous improvement within the existing best practices are the mantra for any global company to be and sustain as a market leader
Local factor conditions such as local demand, existence of supporting and related industries ,infrastructure and governance conditions are very important for any company to cater to global market, hence a perfect strategic plan should be prepared by the company in coherence with all these local factors…
Firms need to employ and retain managers who have the mindset capable of:
-
Indentify and making the most efficient use of resources irrespective of their location.
-
Managing conflicts
-
Managing Change
-
Demonstrating patience and humility
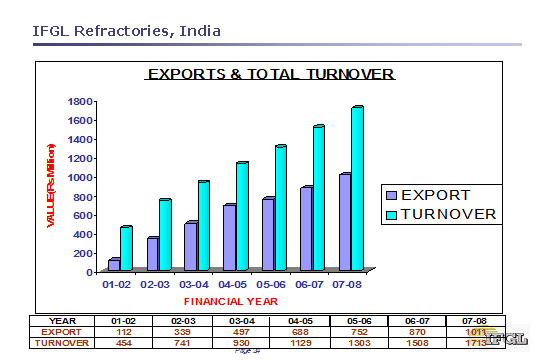
Fig 13
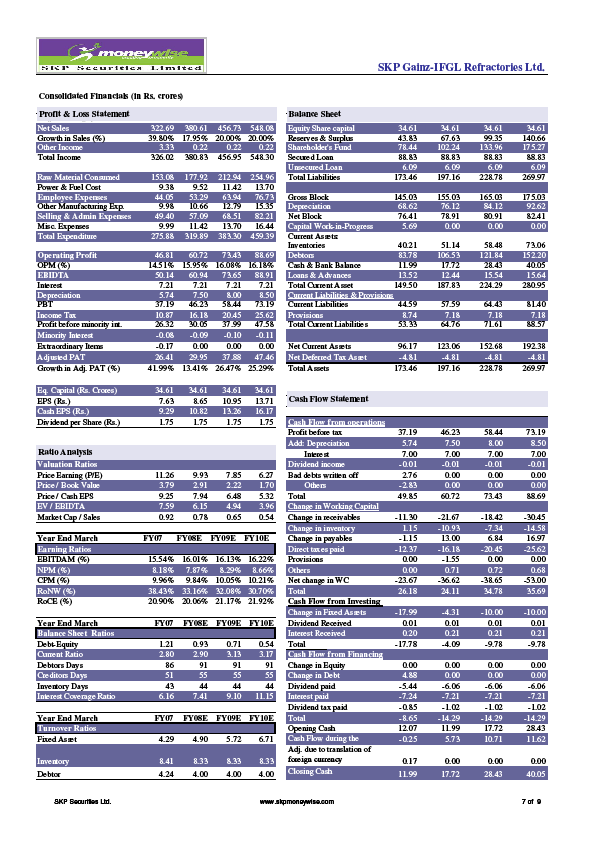
Table 3:IRL Consolidated Financial Data analysis( 2007-2010)
Sources: www.skpmoneywise.com
The Above Table indicates the Consistent growth in the steel industry has helped in increasing the demand for refractories. Organic and inorganic expansions by IRL to meet the growing demand and continuous cost cutting strategies will increase its revenues and overall margins. We expect the company's net sales and PAT to grow at a CAGR-Compound Annual growth rate of 19.31% and 21.58% respectively, over FY07-10.
2.3.1Major Globalization Initiatives from IRL and TRL Companies
* Global marketing strategies by jean-pierre jeannet and H.david Hennessey PP: 586-587
To produce where it is the cheapest and sell where it is the dearest-that’s a global delivery model according to N.R Narayana Murty of Infosys, who has understood and done it. In his words, a global company is one that can produce anywhere and sell anywhere.
The key facets that differentiate truly global companies is their positioning in terms of assets, capabilities, brand and their relative resilience to shocks and even to business cycles. According to Ratan Tata of Tata group of companies a company does not become global by simply participating in a certain number of geographical markets. In that sense it is not a sum of its parts. It is the company’s ability to become globally competitive, leverage global opportunities, and have the required global capabilities that makes it global.
The two biggest factors imparting business in recent times have been the possibilities thrown up by an increasingly globalized world economy(falling tariffs, easy flow of capital across borders, pressure on costs, outsourcing the possibilities of being part of a global supply chain and so on) and the shifting nature of the home market(greater competition, falling consumer finance rates, less government intervention, etc…)
Today Indian companies have learnt how to cut costs and upgrade quality. In most cases this has been against the pressure of duties being cut and foreign competition setting in.
The name India ha become acceptable than before and Indian companies are making serious profits out of their global operations. Some of the best examples in going global in Indian manufacturing have been through acquisitions, moving up value chains and creating infrastructure outside India. Lets us look at a few examples of initiatives from Indian companies going global.
Indoflogate Refractory Ltd…..
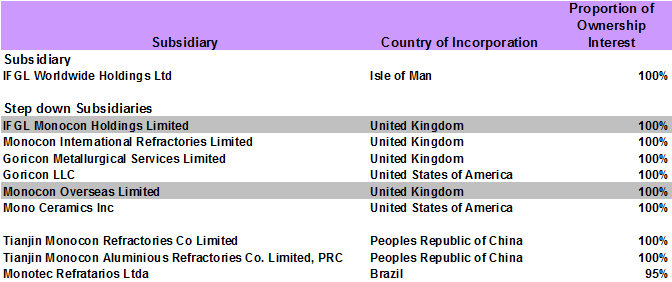
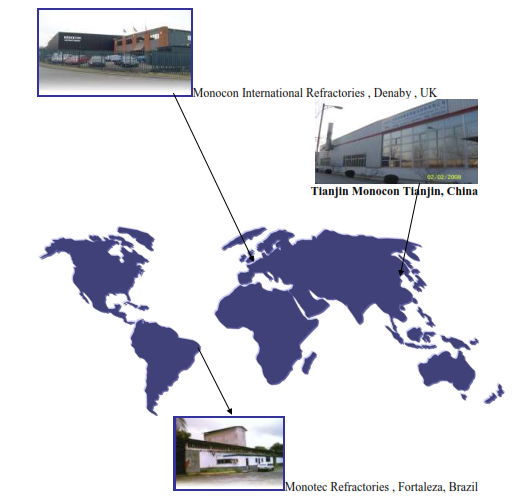
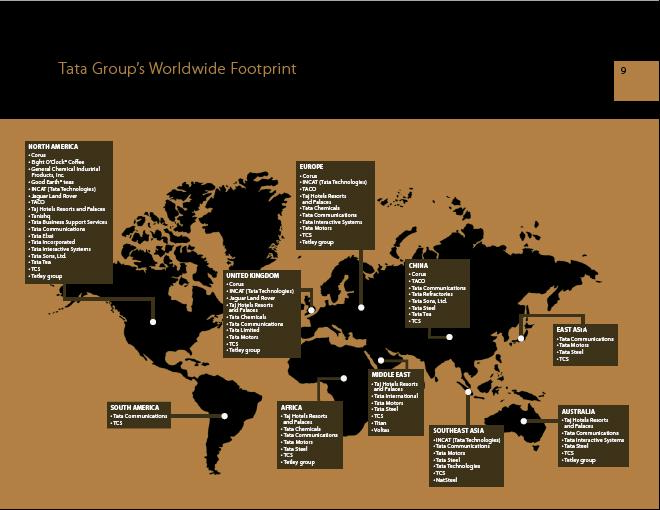
Fig 14..IRL Global operations worldwide
Overseas Operations
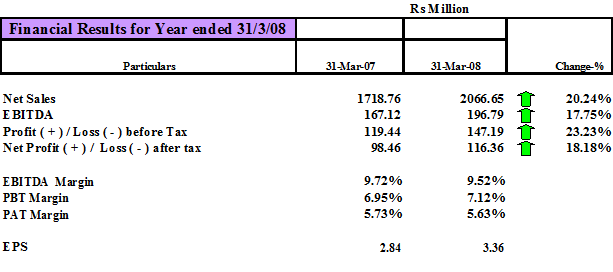
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA)
Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Sources: www.ifglref.com
Table 4…Financial Results of IRL from Overseas Operation
TRL China Ltd.
Tata Refractories has set up a new plant in China to manufacture Magnesia Carbon Refractories. The new plant located at the chemical and metallurgical industrial park area in Bayuquan, Yingkou City in China which is conveniently located about 40 kilometres from raw material sources and 8 kilometres from the seaport facilitating transportation. It was set up at a with a capital investment of Rs. 27 crore. and a production capacity of 30,000 MTPA, this strategic initiative has been taken to leverage the proximity to raw material sources and to avail of the low-manufacturing-cost structure of the Chinese economy. This would not also facilitate smooth supply of cost-effective products to customers across the globe.
Sources: http://www.tata.com/company/Articles/inside.aspx?artid=ejlgELNuj2c=.
The Greenfield plant, located at Bayuquan in Lioning province situated in the north eastern part of China, is the first Greenfield manufacturing unit of TRL as well as of Tata group in China. The plant was inaugurated by the managing director of TRL, C D Kamath on December 28, 2006, coinciding with the birthday of group chairman Ratan. N Tata.
The plant has been commissioned at a record time of exactly eight months, a record in project completion even by Chinese standards. Similarly, TRL has set up a production facility in Gujarat to manufacture bauxite-based Refractories. These strategic initiatives, aimed at making TRL a global Refractories company, are a part of company's expansion and modernization drive launched two years back at a capital investment of Rs 282 crore. This drive has resulted in making the company one of the most modern plants, and has enhanced its capacity to 2,50,000 MTPA, the highest for any Refractories unit under one roof in the world.(source:www.steelworld.com, 2009)
Performance
The Company has two Subsidiary Companies viz. TRL Asia Private Limited (a Special Purpose Vehicle in Singapore) and TRL China Limited, a 100% Subsidiary of TRL Asia Private Limited. Company’s holding in TRL Asia Private Limited is 88%. TRL China started commercial operations from 28th December 2006. TRL China has earned a profit during the first full year of its operation , It has achieved a turn-over of Rs.67 Crores and PBT of Rs.0.63 Crores. Profitability of TRL China has been, however, seriously affected due to withdrawal of VAT benefits by the Chinese Government as well as by the strengthening of Chinese Currency (RMB)- Renminbi against the Dollar. In order to meet market demands, TRL China is undertaking the Phase-II expansion of its production facilities at an estimated capital expenditure of Rs.14.95Crores.
(Source:www.tataref.com)
SWOT analysis of IRL and TRL Companies..
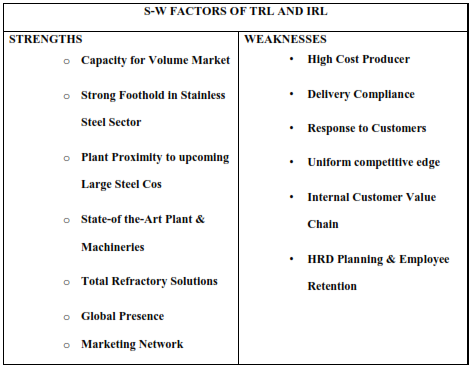
Strategies of IRL and TRL to Handle Major Customers:
-
Strategic alliance for Total Refractories Solution
-
Frequent Technical Workshop and Partnering thru’ awareness programme
-
Collaborative product development program
-
“0” Defect Product offering
-
Improved Order Execution System
-
On-Site Refractories Management System as U.S.P
-
Close watch on Competitors movement
Analysis Of Global Refractory Market
RHI Group
RHI AG is a globally operating industry group based in Vienna, Austria with 30 production sites and employs 7,400 people worldwide. Following the successful sale of the Heraklith Group, the RHI Group is now focusing all activities on first core business, refractories. The RHI share is listed on the Prime Market of the Vienna Stock Exchange (ATX).
Fig 15: RHI Share in the core activities
RHI Activities
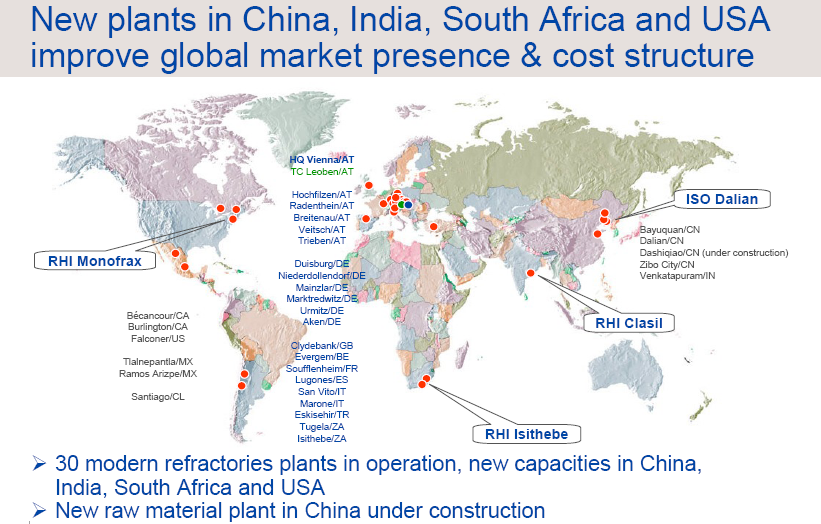
RHI Story of Successful “Turnaround”
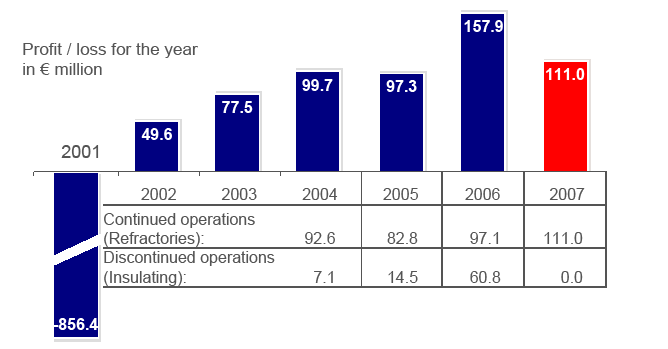
Fig: RHI Financial Success results
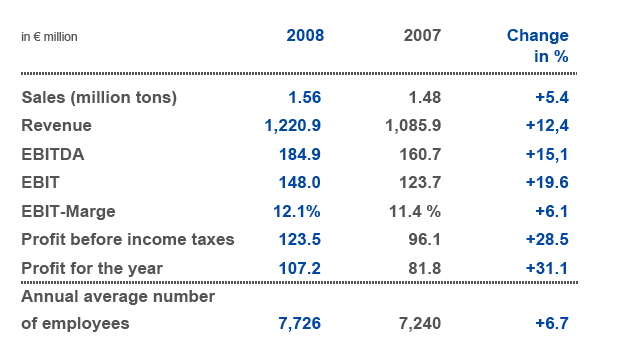
Table 4: RHI Key Figures Q1-Q3(2007-008)
Global Partners for Global Customers
Today RHI is world market and technology leader in refractories. With high quality products, system solutions and services RHI is a competent partner of more than10.000 customers in 180 countries on all continents.
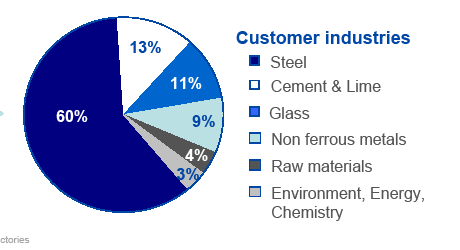
Fig 18: RHI Market Share sector wise
Global Player RHI
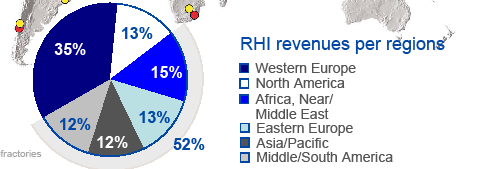
Fig19: RHI revenues per regions
Growth Potential in BRIC and next 11-countries

Established Brands of RHI

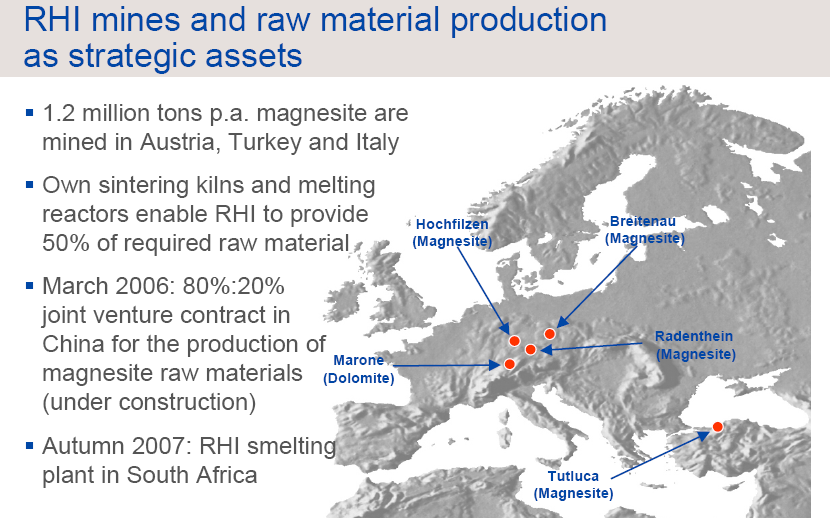
RHI Raw materials as strategic Assets
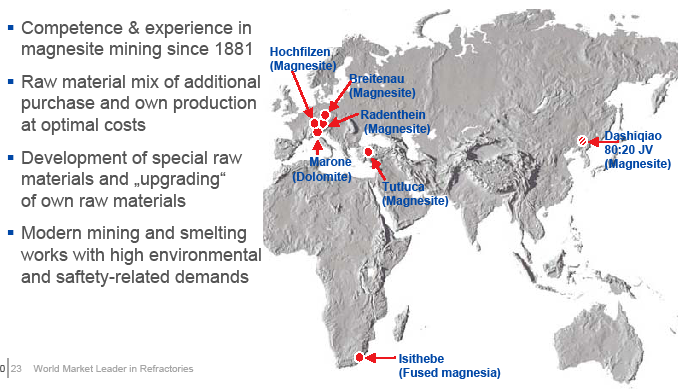
Sources: www.rhi-ag.com
Business Offices:
RHI AG, Corporate Communications
Elke Koch
Wienerbergstrasse 11, 1100 Wien, Austria
Tel: +43(0) 50213-6160, E-Mail: elke.koch@rhi-ag.com
Future Development and Target

Vesuvius Refractory (www.angeltrade.com)
Business Outlook
Vesuvius is part of the Cookson group, which is the world leader in the Refractory business. Hence, Vesuvius is a competitive player in the Indian Refractory space offering technologically superior products compared to peers offering value-added services through total refractory management services to certain steel manufacturers in India.
Further, the Steel Industry, which is the primary consumer of refractory and the target market for Vesuvius, is expected to ramp it production and grow at 10-12% over the next few years. However, the steel capacity additions during the current year have been below target and this puts doubt upon whether the capacity addition targets for the next few years would be achieved due to general economic scenario.
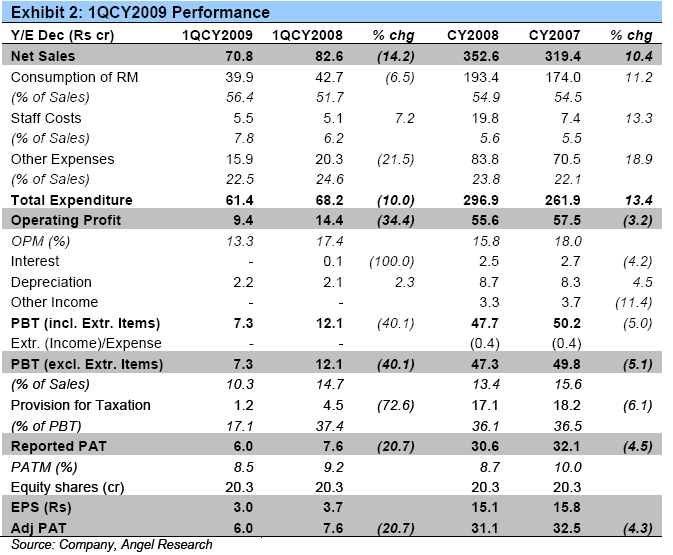
Vesuvius India’s Performance Highlights:
Top-line down 14.2%: Vesuvius India’s (Vesuvius) Top-line declined by 14.2% yoy during 1QCY2009 to Rs70.8cr (Rs82.6cr) on the back of lower Volumes and fall in Realisations. We believe this trend will continue for some more quarters on account of the decline in Realisations.
-
OPM declines by 410bp to 13.3%: During 1QCY2009, the company’s Operating Profits stood at Rs9.4cr (Rs14.4cr), down 34% yoy. The company’s OPM fell by 410bp during the quarter to13.3%. We believe that OPMs fell primarily due to higher proportion of Sales coming from lower-Margin unshaped products.
-
Bottom-line de-grows 20.7%: The company’s Net Profit for 1QCY2009 fell by 20.7% to Rs6.0cr (Rs7.6cr). For CY2008, the company’s Net Profit fell by 4.5% to Rs30.6cr (Rs32.1cr). The company booked Extraordinary expenses of Rs0.4cr during the quarter excluding which Net Profit fell 3.3%.
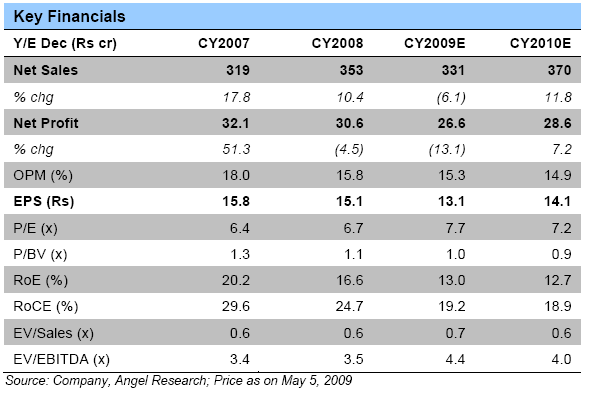
ROE-Return on equity
ROCE-Return on Capital employed
Price-Book value-P/BV- valuation ratio and is arrived at by dividing the market price of a share with the respective company's book value per share
Price-Earning Ratios-P/E- For example, if a company is currently trading at $43 a share and earnings over the last 12 months were $1.95 per share, the P/E ratio for the stock would be 22.05 ($43/$1.95).
Operating Profit Margin-OPM
Russian Refractory (www.eastcapital.ru)
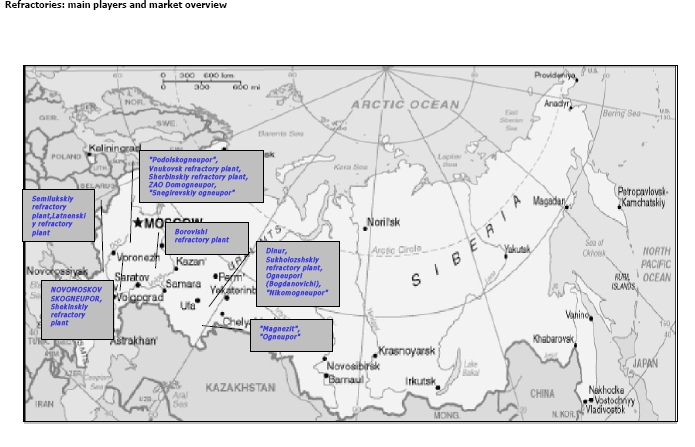
Refractories: main players and market overview
The capacity of the world’s refractory market in natural terms exceeds 23 mln. tons, in dollar terms – more then $15 bln. The world’s largest consumers are: China, CIS –commonwealth Independent state and North America.
Iron and steel production consumes more than 55% of the total demand for refractories: therefore, the profitability of the refractories industry as a whole is strongly influenced by steel production levels and steel plant investments.. Refractory industry development is directly connected with development of an iron and steel industry which provides mass introduction of alternative and energy-saving technologies. Refractory products have changed over the years, from the making of simple firebrick a century ago to today's technically complex brick and monolithic products. The success of these products has changed the industry's sales cycle, as customers are now able to put off replacing their ladles and furnace linings because of these better-engineered products. Longer-life, more efficient kiln and vessel bricks have added months to the steel and cement industry's production run times and have increased capacity.
Europe is self-sufficient in only a few refractory raw materials, so there is a substantial requirement for imports of key materials. China, representing more than 40% of world’s production and consumption is a major supplier of many relatively inexpensive refractory raw materials. However, increasing demand from China’s own industries has restricted exports of many raw materials, including magnesia, bauxite, alumina and silicon carbide. This situation has led to shortages in some cases and consequent price increases. Increasing oil prices have also negatively impacted prices for raw materials. In terms of refractories supply, the Chinese market is the main focus currently as it has the fastest growing steel industry. However, volume wise, refractory consumption is not increasing as rapidly as might be expected because of the increased use of modern steel process routes that require a shift from low-grade fireclays to high grade products. Over recent years there has been considerable consolidation within the refractories industry.
The two largest refractories groups, RHI (formerly Veitsch-Radex Didier) and Vesuvius (owned by Cookson plc), both made several acquisitions, taking over Harbison-Walker and Premier/Hepworth respectively, as well as several smaller companies. In 2003, RHI had an estimated 11% share of the worldwide market, and Vesuvius had around 9% of the total.
Overall growth in steel production in Western European for the period 2003– 2007 is expected to average 1.6% per year, with high growth in 2004 and less towards the end of this period. East European steel production should continue to show healthy growth in this period. These factors will have an impact on the demand for refractories
EU (European) Refractory Robin Schmidt-Whitley, European Refractories
Robin Schmidt-Whitley, European Refractories
Producers Federation PRE, Trade and Raw Materials Imports, 25th Sep 2008
The EU Refractories Industry Profile:
The EU refractories industry is a comparatively small industry within the Ceramics sector:
-
Workforce 26.000
-
Sales 4 billion € (19 % of world market)
-
Production 6 million tons of bricks and monolithics
The industry is highly exposed to international competition:
-
Exports 32 % (worldwide)
-
Imports 10 % (mainly from China)
Refractories are of strategic importance to the EU materials industries
The Strategic Importance of Refractories
A domestic refractories industry is of strategic importance for Europe Refractories are irreplacable as linings of furnaces wherever industrial processes surpass temperatures of approx. 600°C
-
Without refractories, there would be no materials industry
-
No steel, no glass, no cement, no aluminium, no copper, no building bricks, no porcelain, no cars, no electricity...
-
Example: Copper Converter *
Some Facts on Refractory Raw Materials
Raw materials are a major concern for the refractories industry.
-
Raw materials account for some 40% of the cost of refractories finished products (bricks and monolithics)
-
Raw materials have a major influence on product quality
-
The refractories industry relies heavily on imports of raw materials
-
China has become the main supplier of many high volume raw materials
Sources of some Important Refractory Raw Materials
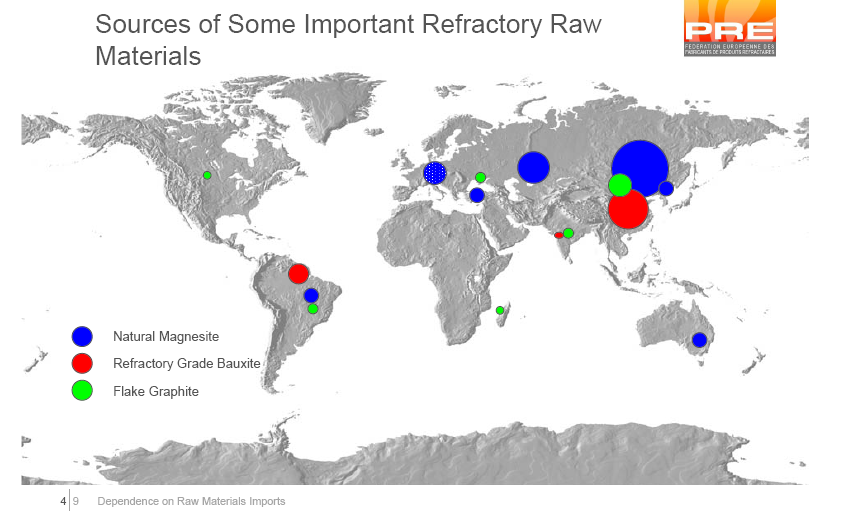
The Domination of China
There are only a few refractory raw materials available in Europe, i.e. fireclay, silica, and alusite, dolomite, and some types of magnesite. But for many qualities China is the main source and supplies the World:
-
dead burned magnesia 45%
-
fused magnesia 90%
-
refractory bauxite 95% *
-
silicon carbide 40%
-
brown fused alumina 50%
-
graphite 80%
* including Guyana controlled by China
Price Dependence on China
The price evolution of refractory raw materials* seems to be greatly influenced by the degree of dependence on Chinese sources:
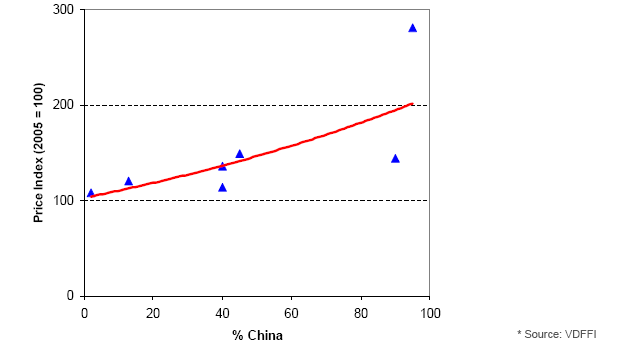
China's Raw Materials Policy is Unfair
-
Exports of raw materials such as dead burned magnesia, refractory bauxite, and graphite are restricted and heavily taxed
-
Examples:
-
the total quantity of magnesia available for export is reduced annually
-
demand now exceeds export supply
-
export licenses are auctioned to selected domestic bidders only
-
due to shortage, the export license cost by far exceeds the issue price
-
output VAT of 17% is raised (from September '06)
-
export tax on top: magnesia 10% - bauxite 15% - graphite 20%
-
minimum export tax for magnesia (from March '08)
-
None of these costs are borne by Chinese domestic producers, and exports of finished products made from these raw materials are not taxed
Competitive Advantage of EU Industry
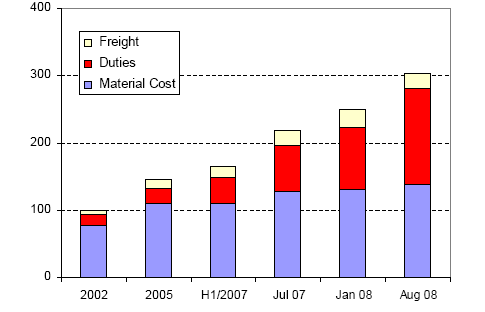
Since 2002, magnesia prices have increased by 80% in China and by more than 200% for international buyers. Due to licensing and taxation of exported raw materials, Chinese domestic producers of magnesia bricks have a cost advantage in European and export markets of approx. 30%
Conclusions and Priorities
-
The EU refractories industry is heavily dependent on raw materials imports, especially from China
-
Exports of raw materials from China are restricted and heavily taxed
-
Domestic Chinese producers enjoy an important competitive advantage
So what are the priorities?
Short Term:
-
Ensure access to raw materials at identical conditions to competition
-
If this is not possible, countermeasures should be taken
Long Term:
-
Develop alternative raw materials sources
-
Increase worldwide exploration of raw materials
Findings of the Study
This section provides a discussion of the findings of the study. At first, the characteristics of the sample are de






























