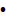Learn Python Programming Fundamentals: A Beginner’s Guide [Updated 2020]

Python is one of the powerful, high-level, easy to learn programming language that provides a huge number of applications. Some of its features, such as being object-oriented and open source, having numerous IDE’s, etc. make it one of the most in-demand programming languages of the present IT industry.
According to TIOBE index, as of January 2020, Python is one of the popular programming languages. By looking at the popularity of this programming language, many IT professionals, both beginners as well as experienced alike, are willing to build their career as a Python developer.
Image source
Many people have daunting questions like:
 How one can start to learn Python?
How one can start to learn Python?
 What are the fundamental concepts you need to know to learn Python?
What are the fundamental concepts you need to know to learn Python?
With an aim to help similar concerns, Simpliv is presenting this blog to discuss about the various fundamental concepts of Python programming and take you along to start writing Python programs on your own.
Before proceeding further, at this point, we would like to suggest that you read blog (first blog in this series) on introduction to Python programming language.
Without further ado, let us quickly look at the topics we will be covering in this blog:
 How to install Python
How to install Python
 Basic syntax
Basic syntax
 Python identifiers
Python identifiers
 Python reserved words
Python reserved words
 Indentation
Indentation
 Quotations in Python
Quotations in Python
 Comments in Python
Comments in Python
 Using Blank lines
Using Blank lines
 Constructs
Constructs
 Python Variables
Python Variables

 Python Data Types.
Python Data Types.
Let us look at the 8 Steps to install Python
Let us start by learning the steps to install Python. The following are the steps need to be followed while installing Python on Windows:
Step 1:
Download python.exe or zip bundle from Python official website https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/.
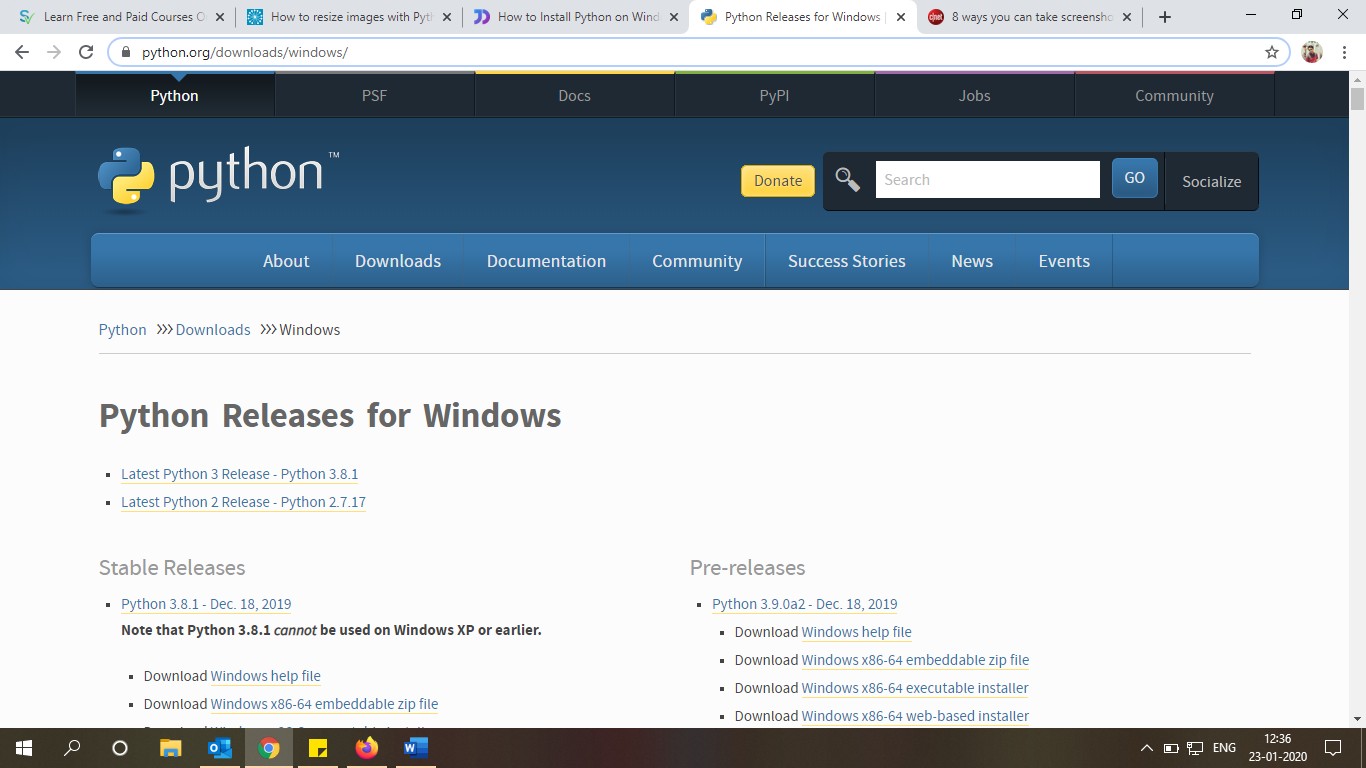
Step 2:
Select Downloads and download python.exe file for Windows.
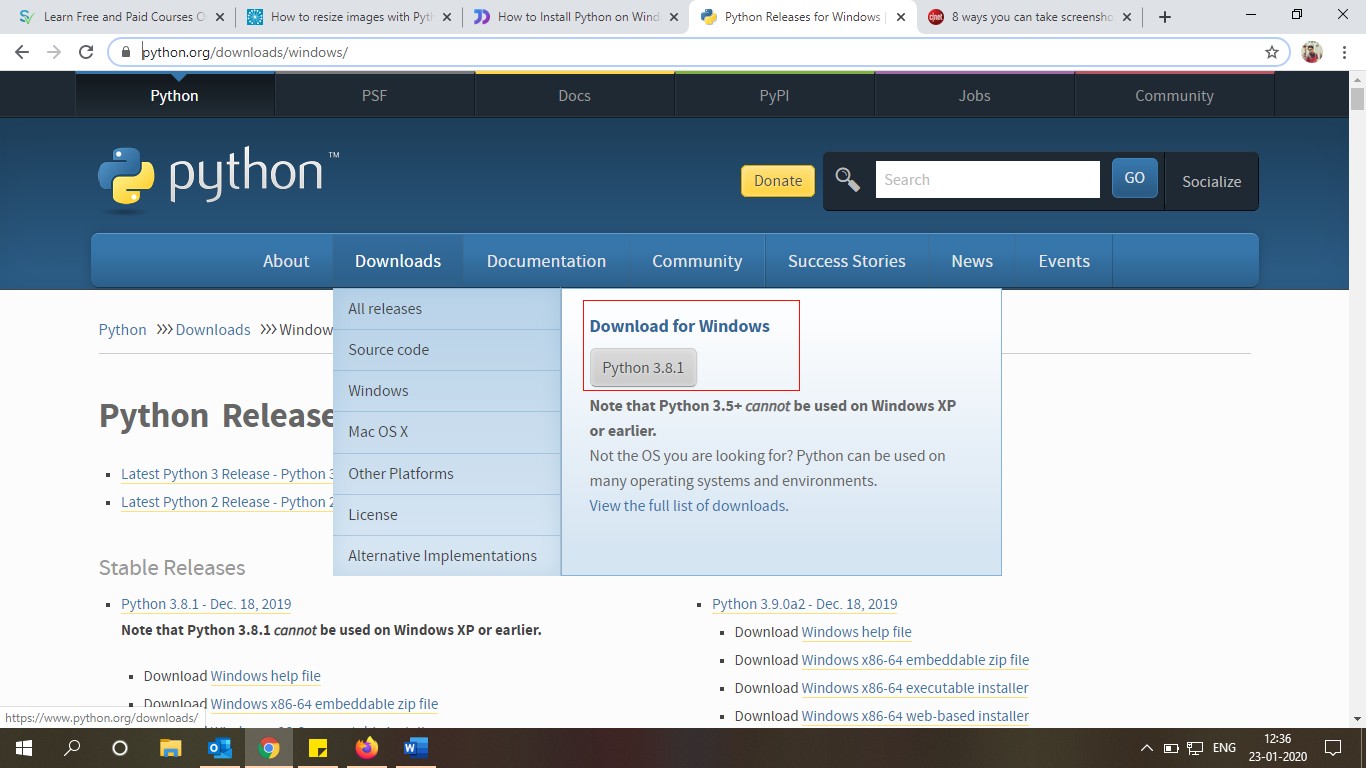
Step 3:
Once the installer is downloaded, run the Python installer. Check on Install launcher for all users.

Step 4:
Select Customize installation. Check on all settings Document, pip, tcl/tk, python test suite, py launcher, for all users. Click on Next.
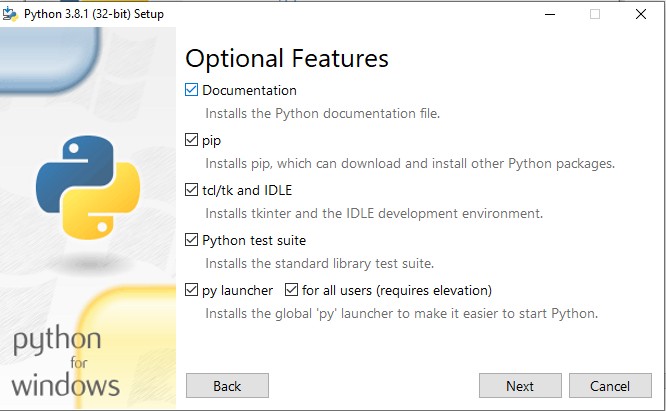
Step 5:
This takes you to Advanced Options available while installing Python. Here, select the Install for all users and Add Python to environment variables check boxes.
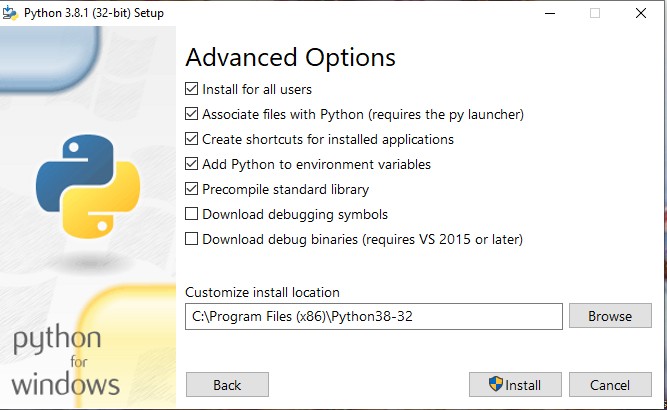
Step 6:
Once installation is done, you can see that the installation is successful.
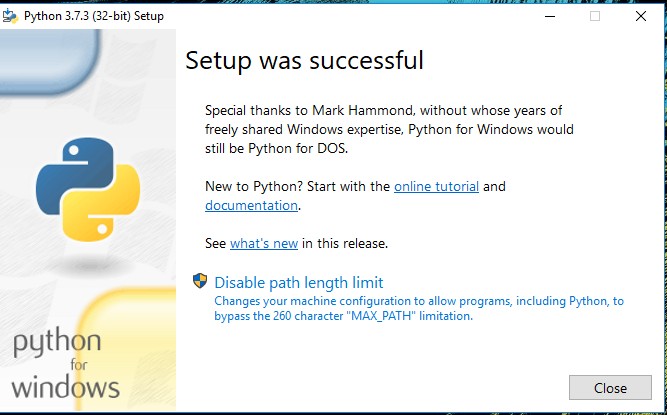
Step 7:
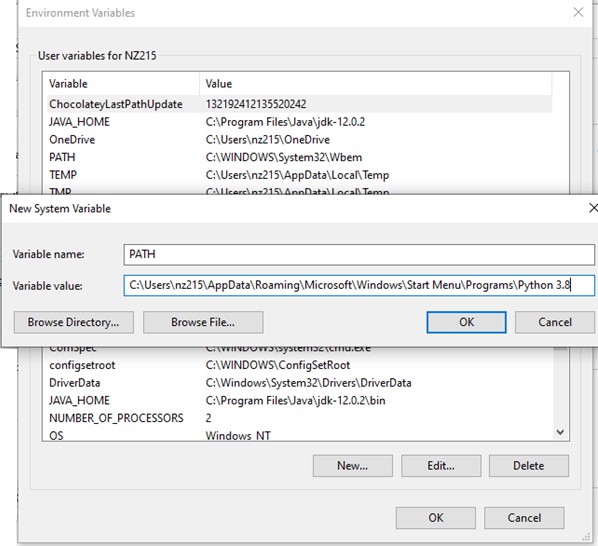
Add Environment variables to run Python in Windows.
In the Start menu, search for “advanced system settings”. Select “View advanced system
settings”. In the “System Properties” window, click on the “Advanced” tab and then click on the “Environment Variables” button.
Locate the Python installation directory on your system. If you followed the steps exactly as above, Python will be installed in below locations:
 C:\Program Files (x86)\Python37-32: for 32-bit installation
C:\Program Files (x86)\Python37-32: for 32-bit installation
 C:\Program Files\Python37-32: for 64-bit installation.
C:\Program Files\Python37-32: for 64-bit installation.
Step 8: Verify Python Installation
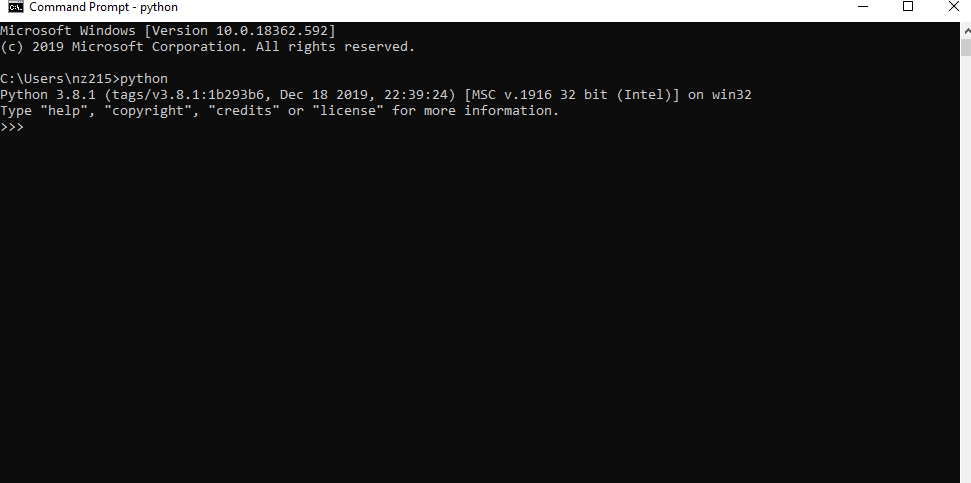
You have now successfully installed Python 3.8.1 on Windows. You can verify if the Python installation is successful through the command line.
Search for the command prompt and type “python”. You can see that Python 3.8.1 is successfully installed.
Basic syntax to write a Python program
Once you have installed Python software successful into your system, you can start writing Python program in the command prompt.
Python has many similarities and differences with other programming languages such as Perl, C, and Java, etc. Let us discuss the basic syntax to write a Python programming language.
Python provides two ways to run a program, and they are:
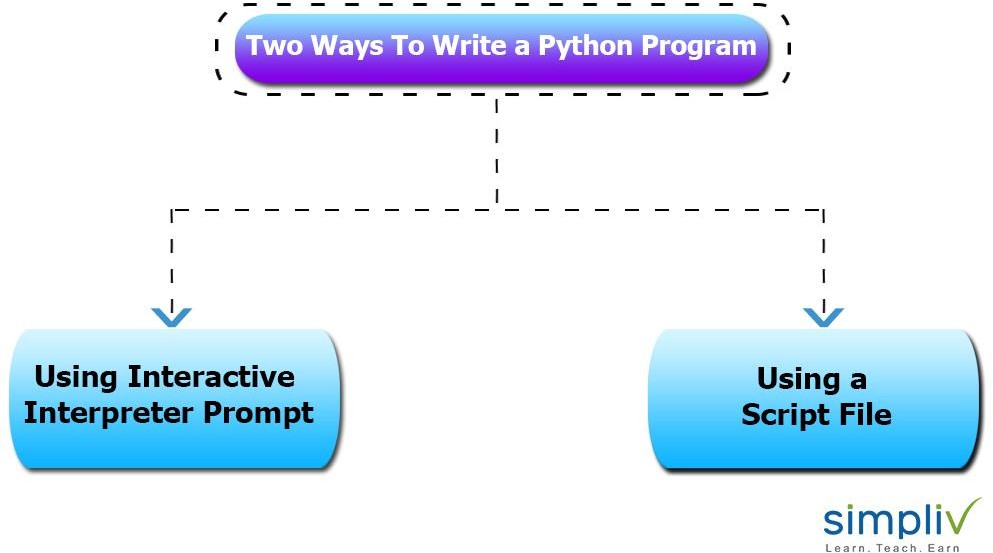
 Using Interactive interpreter prompt
Using Interactive interpreter prompt
 Using a script file.
Using a script file.
We will discuss both of these separately in detail. Here in the below discussion, we will write a program to get the output as Hello world
 Using interactive interpreter prompt:
Using interactive interpreter prompt:
Using interactive prompt, users can execute the Python statement one by one. This mode of execution is preferred where the users are concerned about the output of each line of the Python program.
In Python3 print() function is used to print the message in the console. It is one of the standard functions used to print the output to the console.
Invoking the interpreter without passing a script file as a parameter brings up the following prompt –
Type the following text at the Python prompt and press Enter –

Now you will get the output as:

In this program, we are using built-in print() function to print the string Hello world as the output. String is a sequence of characters and in Python they are enclosed inside single quotes (‘’) , double quotes(“ ”) or in triple quotes(“”” “””).
If you want to print a list of five colors, you can write the program in the Python prompt as follows:

Now you will get output as:

 Using a script file:
Using a script file:
The program can be written in a script. Python files have extension .py. You can write the code in a file and that can be executed later. Users can write the code using the editor and then save it with .py extension. For example, you can save the file with the extension myfirstprogram.py
To print Hello world we can write the code Print (“Hello world”);
In order to rub this myfirstprogram.py file, we need to run the command $ python3 first.py on the terminal.
Now the output message displays as Hello world on the console.
Python Constructs
Now let us see some useful Python Constructs that provide a better idea of structure of Python code.

 Functions
Functions
- Classes
- Modules
- Packages
- Lists.
1. Functions:
In Python programming language a function is referred to as a collection of statements grouped under a name. You can use it whenever you there is a need to execute all those statements at a time. You can call the function as many times as you want it in your program. Function may return a value.
2. Classes:
Python is an Objected Oriented programming language. This language supports classes and objects. A class is an abstract data type. An object is a real world entity and an instance of a class.
3. Modules:
A collection of related classes and functions can be called as a module. These are some of the different types of modules:
-
- mathematical calculations
- string calculations
- web programming, etc.
4. Packages: Python package is a collection of related modules. Developers can either import a package or can develop their own.
5. Lists: Lists can be a collection of values. They are declared in the CSV (Comma Separated Values) format and enclosed in square brackets.
Python identifiers:
Python identifier is a name that is used to identify a variable, function, class, module or other object. It helps to differentiate one entity from another.
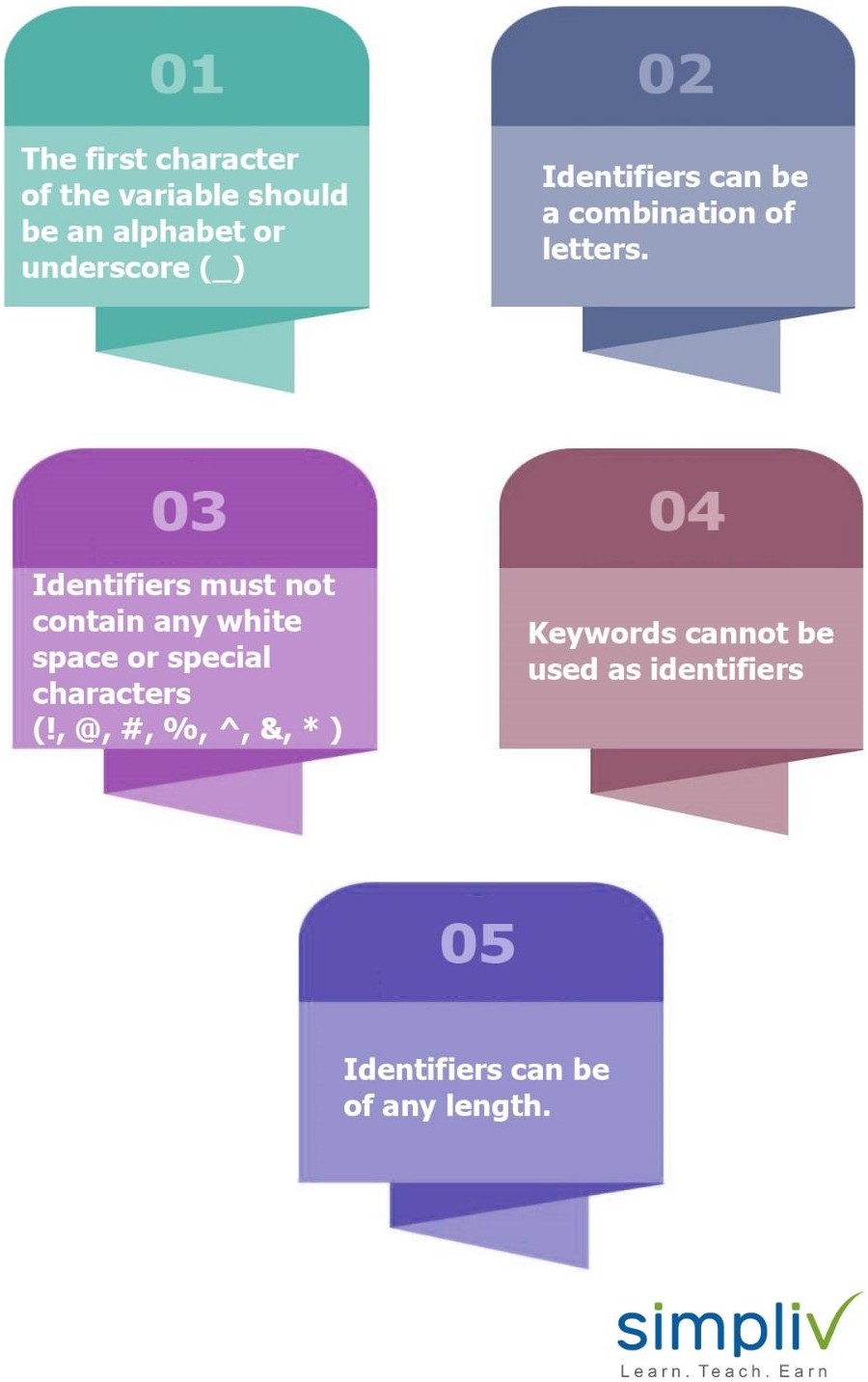
Some of the rules for writing identifiers are as follows:

Did You Know?: “Python is a case-sensitive language. In Python myname and Myname are not the same.”
-
- The first character of the variable should be an alphabet or underscore (_)
- Identifiers can be a combination of letters. They can be written in lower case (a to z) or upper case (A to Z) or in digits (0 to 9) or an underscore(_). For example: Names like myFirstprogram, var_1, display_this_on_screen etc.
- Identifiers must not contain any white space or special characters (!, @, #, %, ^, &, *)
- Keywords cannot be used as identifiers
- Identifiers can be of any length.
Python Reserved words (Python keywords)
Python keywords are the reserved words. These keywords are used to convey a special meaning to the compiler/interpreter. Keywords cannot be used as a variable name, function name or any other identifier.

Did You Know?: “Python 3.7 has 33 keywords and the number can vary slightly in coming days.”
All the keywords in Python are lowercase except True, False and None. The following table gives the list of keywords used in Python.
|
True
|
False
|
None
|
and
|
As
|
|
assert
|
break
|
Continue
|
for
|
Lambda
|
|
try
|
from
|
Nonlocal
|
while
|
Del
|
|
global
|
not
|
With
|
elif
|
If
|
|
or
|
yield
|
Assert
|
else
|
Import
|
|
pass
|
break
|
Except
|
in
|
Raise
|
|
finally
|
is
|
Return
|
|
|
The above table provides a list of keywords. However, the list may get vary according to different Python versions. You can type the following in the prompt to get the list of all the available keywords in the current version of Python being used.

Now you will get the output of all the available keywords in your Python version.
Indentation
Some of the programming languages such as Java, C, etc. use braces { } to define the block of code. But Python uses indentation.
The number of spaces is variable, but it should be noted that all the statements within the block must be indented the same amount. The usage of indentation makes the Python code look neat and clean.
Generally, four whitespaces are used for indentation and that is preferred over using tabs. The following code is an example of indentation:
Program:

Incorrect indentation will result in IdentationError
Quotation in Python
To denote string literals Python accepts single (‘), double (‘’), triple (‘’’) quotes as long as the same type of quote starts and ends the string.
The below example shows how to use quotations in Python.
|
single_quotation
|
‘word’
|
|
double_quotation
|
“Python is a powerful programming language”
|
|
triple _quotation
|
“””Python is a powerful programming language. It is open-source, and object oriented programming language”””
|
Comments in Python
Comments play a very important role while writing a program. It describes the program to the user so that they can easily understand the program.
In Python hash (#) is used to start writing a comment. The interpreter does not interpret the comment.
Python supports two types of comments. They are:
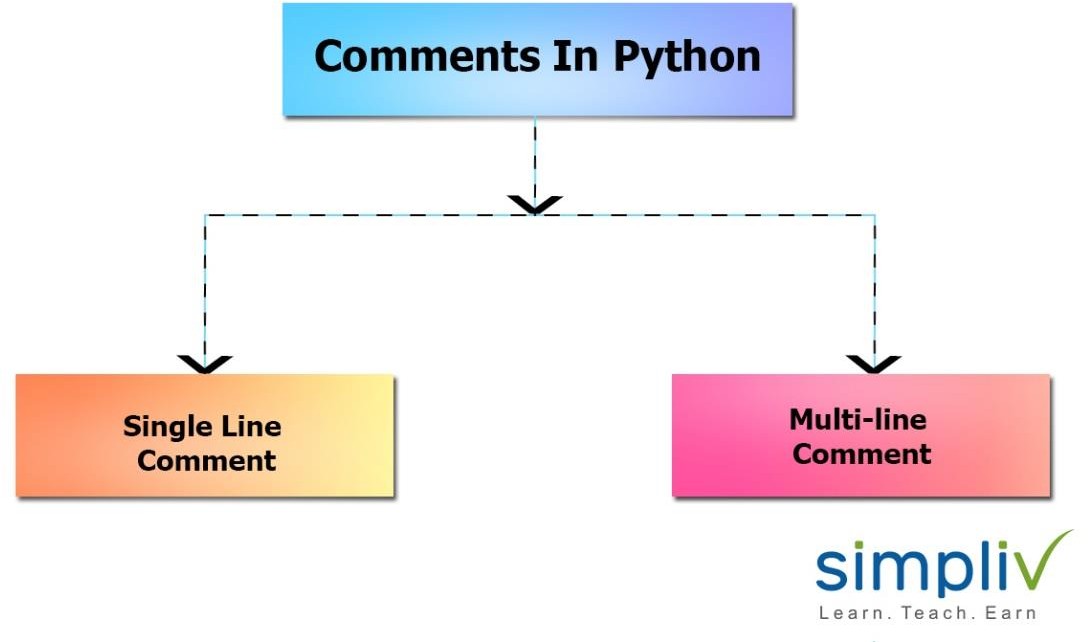
- Single Line Comment.
- Multi-Line Comment.
1. Single Line Comment:
Single Line Comment starts with ?#?
The following program has single line comment.

Once the above program is executed, we get the following output:

Here you can note that only the output Hello world is displayed on the console as the output and the above comment written with # tag is not displayed.
2. Multi-Line Comment:
Developers can write multiple lines of comments to their code. It can be done in two ways. They are:
-
- By using # tag before start of each line of comment
- By using triple comment at the start and at the end of the comment. We will see a program example for these types below.
 Using # tag:
Using # tag:

Once the above program is executed, we get the following output:

Here in the above output, you can note that only Hello world is displayed on the console as the output and the above comments written with # tags are not displayed.
 Using triple quotes:
Using triple quotes:

Once the above program has been executed, we get the following output:

Here, you can note that only the output Hello world is displayed on the console as the output and the above comment given using triple quotes is not displayed.
Using Blank Lines
In Python, a line containing only whitespaces, possibly with a comment, is treated as a blank line and Python totally ignores it.
Python Variables:
The names that are used to refer memory locations are called variables. These are nothing but the reserved memory locations to store values. They are also known as identifiers and are used to hold value.
In Python, the interpreter allocates memory based upon the data type of a variable and decides what can be stored in the reserved memory.
Variable names can be a group of both letters and digits. These names have to start with a letter or an underscore.
The following is an example for a variable.
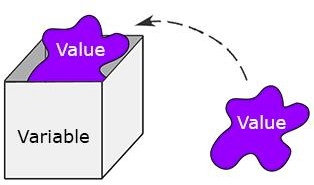
Here in this above example, we have created a variable named number and assigned value of 30 to it. Variable can be understood as a container that is used to hold numbers.
Now let us see how to assign a value to a variable.
In Python programming language, there is no need to give an explicit declaration to reserve memory space. The declaration is done automatically whenever you assign a value to a variable.
Python is a type inferred language; it means Python can automatically understand the variable type.
The (=) operator variable is used for assigning value to a variable. The operand to the left of the operator (=) is the name of the variable and operand to the right of the operator (=) is the value stored in the operator.
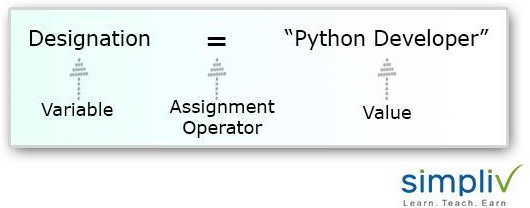
The following program is an example of how to assign values to a variable.

Here a, designation and salary are the variables and 10, Python Developer and $113,778 per year are the values to them respectively.
|
Variables
|
Values
|
|
a
|
10
|
|
Designation
|
Python Developer
|
|
salary
|
$113,878
|
The output of the above program will be:

Multiple assignment
Python programming language allows the developers to assign values to multiple variables in a single statement that is also known as multiple assignment.
Multiple assignment can be applied in two ways: assigning single value to multiple variable or assigning multiple values to multiple variables.
We will see programmatically how multiple assignments are done in two ways.
1. Assigning single value to multiple variables

The output of this programming will be as below:

Here all the three variables a, b, c have been assigned a single value i.e. 10.
2. Assigning multiple values to multiple variables

The output for the above program will be as follows:

Here the integers objects with values 10, 20, 30 are assigned to variables a, b, c respectively.
|
Variables
|
Values
|
|
a
|
10
|
|
b
|
20
|
|
C
|
30
|
Python Data Types
Each value of Python has a data type. Variables can hold values of different data types. Python allows the