CONCEPT AND METHODS OF THE FINANCIAL
STATEMENT ANALYSIS
Aiming to detect changes in the company’s development trends in order to make more successful economic decisions, the financial statement analysis (also referred as the financial analysis of enterprise) is the process of analyzing and reviewing firm’s balance sheet (statement of financial position), income statement (profit and loss report) and other statements. It allows to estimate the company’s overall performance by calculating and comparing a complex of indicators, building the trend lines and making conclusions on the business health and sustainability. The motivation for applying the financial statement analysis to the annual report of a company is different for each group of users. Creditors are normally interested in estimating the creditworthiness of borrowers, investors want to measure the revenue their potential investments can bring, and managers are willing to have the most precise information on the financial position and performance of their companies.
Despite apparent difference in motivation, all the above-mentioned users have common objectives in the financial statement analysis. They are following:
1. Reviewing the company’s performance over past periods. Building the trend lines, calculating ratios and indicators with the use of the company’s past financial report is a key to making conclusions on its possible future performance. For creditors and investors reviewing the profitability, activity and liquidity ratios from previous periods can be a base for consideration of their further cooperation with a firm, while for the company managers it may be a reason for some serious economic decisions.
2. Assessing the current financial position. Analyzing company’s current balance sheet and income statement is the most effective way to estimate the condition of a company here and now. Reviewing firm’s assets and liabilities, checking the profitability margins for the current period is necessary for all the users in terms of operative and long-term decision making.
3. Forecasting the profitability trends. As the main goal of every business is the generation of revenue for its owners and investors, planning the company’s cash flows and using analytical methods of forecasting the profitability is highly important for every user of financial analysis. Profitability forecasts is a strong base for investors’ consideration of the alternative ways of using their funds.
4. Forecasting financial failure. One of the most important assumptions that can be made during the analysis of the company’s financial report is measuring a chance of its possible bankruptcy. This factor is vital to a business, and thus should be under a tight control of company’s management, while for investors and creditors financial distress forecasts work as a warning sign.
There are two key methods of the financial statement analysis. First includes an application of the horizontal and vertical analysis to the financial statements of a firm, second is a process of miscellaneous financial ratios calculation.
Horizontal financial statement analysis means the comparison of the information from the financial report of a company over some certain time periods. Both the financial information and the ratios derived from it can be compared. In other words, horizontal analysis (very often referred as trend analysis) is reviewing and comparing the dynamics of the same indicators and making conclusions on company’s performance over time. As said before, this analysis method may be applied the financial statement information itself and to ratios derived from it, so the horizontal analysis may include either absolute values comparison or percentage comparison. Ratios and indicators of a company can also be compared to average values in the economic sector or values of competitors.
Vertical analysis is a process of comparison of one item to the base item. Commonly, the vertical analysis is conducted for the financial statement of a single period (unlike the horizontal analysis, which is reviewing information over at least two different periods of time, or more). Also referred as common-size analysis, vertical analysis commonly means usage of total assets or total liabilities or shareholders’ equity as base figures of the proportion. Main reason for performing the vertical analysis for one single period is seeing the relative proportions of different elements of assets and sources of finance.
The second method of the financial statement analysis is ratios calculation and interpretation. Many ratios showing the relative size of one number in relation to another exist, and being able to measure them and see their dynamics over time is extremely useful in terms of understanding firm’s performance and position.
Most of the ratios can be calculated from the information obtained from the company’s financial statements. They can be used for analyzing trends and comparing firm’s financial condition with previous periods or with other firms. Normally, financial ratios can also be a base for predicting the company’s possible insolvency or bankruptcy.
However, use of financial ratios has some limitations, such as following:
-
A comparison with previous periods or similar-sized companies should be made, since most ratios by themselves do not provide enough information to make conclusions;
-
When available, average values should be used for calculations, since year-end values may not be representative.
All ratios used in the process of the financial statement analysis can be grouped to sets, depending on their goal. Each set allows to approach firm's performance from a different angle and in complex they provide an analyst with a full understanding of the company's financial condition.
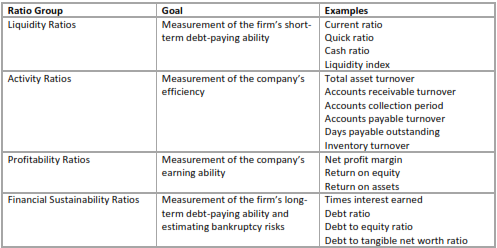
Table 1. Groups of the financial statement analysis ratios
In assumption it can be stated that financial statement analysis means usage of different methods of emphasizing the comparative and relative importance of the data, presented in the financial report of a company to evaluate the company’s performance and position. These methods include horizontal and vertical analysis, calculation of various ratios, studying and interpreting their values to make right conclusions on the business.




