Output

size of union = 32
size of structure = 40
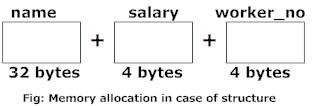
There is difference in memory allocation between union and structure as suggested in above example. The amount of memory required to store a structure variables is the sum of memory size of all members.
But, the memory required to store a union variable is the memory required for largest element of an union.
What difference does it make between structure and union?
As you know, all members of structure can be accessed at any time. But, only one member of union can be accessed at a time in case of union and other members will contain garbage value.
#include <stdio.h>
union job {
char name[32];
float salary;
int worker_no;
}u;
int main(){
printf("Enter name:\n");
scanf("%s",&u.name);
printf("Enter salary: \n");
scanf("%f",&u.salary);
printf("Displaying\nName :%s\n",u.name);
printf("Salary: %.1f",u.salary);
return 0;
}





