eggs hatch in freshwater, and the resulting larvae
and help organize various healthcare workers to
infect snails. When the snails shed these larvae,
bring the disease under control.
the larvae attach to and penetrate human skin.
They feed, grow, and mate in the human
Disease reservoirs. The reservoir for a disease is
bloodstream; the damage to human tissues
the site where the infectious agent survives. For
caused by the accumulating schistosome eggs
example, humans are the reservoir for the measles
with their sharp spines results in disease
virus because it does not infect other organisms.
symptoms including diarrhea and abdominal
pain. Liver and spleen involvement are common.
Animals often serve as reservoirs for diseases
Another disease due to a helminth is trichinosis,
that infect humans. Infectious diseases that can
caused by the roundworm Trichinella spiralis.
be transmitted from animals to humans and
This infectious agent is typically ingested in
from humans to animals, zoonoses, are thought
improperly cooked pork from infected pigs. Early
to account for more than 60 percent of emerging
disease symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea,
infectious diseases today. The major reservoir for
and fever; later symptoms include intense muscle
Yersinia pestis, the bacteria that causes plague, is
pain because the larvae grow and mature in those
wild rodents. There are also nonliving reservoirs.
tissues. Fatal cases often show congestive heart
Soil is the reservoir for many pathogenic fungi
failure and respiratory paralysis.
as well as some pathogenic bacteria such as
Clostridium tetani, which causes tetanus. More
Prions. During the past three decades, evidence
recent examples of zoonotic infectious diseases
has linked some degenerative disorders of the
include hantavirus and severe acute respiratory
central nervous system to infectious particles
syndrome (SARS). Scientists and epidemiologists
that consist only of protein. These “proteinaceous
are now studying the “one-health” concept, which
infectious particles” have been named prions
emphasizes the unity of human and animal
(pronounced pree-ons). The known prion diseases
infectious diseases (Morens and Fauci, 2012).
include Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (in humans),
scrapie (in sheep), and bovine spongiform
Modes of transmission. Infectious agents may
encephalopathy (“mad cow disease” in cattle);
be transmitted through either direct or indirect
all known prion diseases frequently result in
contact. Direct contact occurs when an individual
brain tissue that is riddled with holes. While
is infected by contact with the reservoir, for
22
example, by touching an infected person,
washing, or preparing foods, is a significant
ingesting infected meat, or being bitten by an
form of indirect transmission, especially for
infected animal or insect. Transmission by direct
gastrointestinal diseases such as cholera, rotavirus
contact also includes inhaling the infectious agent
infection, cryptosporidiosis, and giardiasis.
in droplets emitted by sneezing or coughing and
contracting the infectious agent through intimate
These modes of transmission are all examples of
sexual contact. Some diseases that are transmitted
horizontal transmission because the infectious
primarily by direct contact with the reservoir
agent is passed from person to person in a group.
include ringworm, AIDS, trichinosis, influenza,
Some diseases are also transmitted vertically;
rabies, and malaria.
that is, they are transmitted from parent to child
during the processes of reproduction (through
Indirect contact occurs when a pathogen can
sperm or egg cells), fetal development, or birth.
withstand the environment outside its host
Diseases in which vertical transmission occurs
for a long period of time before infecting
include AIDS, Group B strep infection, and
another individual. Inanimate objects that are
herpes encephalitis (which occurs when an infant
contaminated by direct contact with the reservoir
contracts the herpes simplex type II virus during
(for example, a tissue used to wipe the nose of
vaginal birth).
an individual who has a cold or a toy that has
been handled by a sick child) may be the indirect
Role of Research in Prevention
contact for a susceptible individual. Ingesting
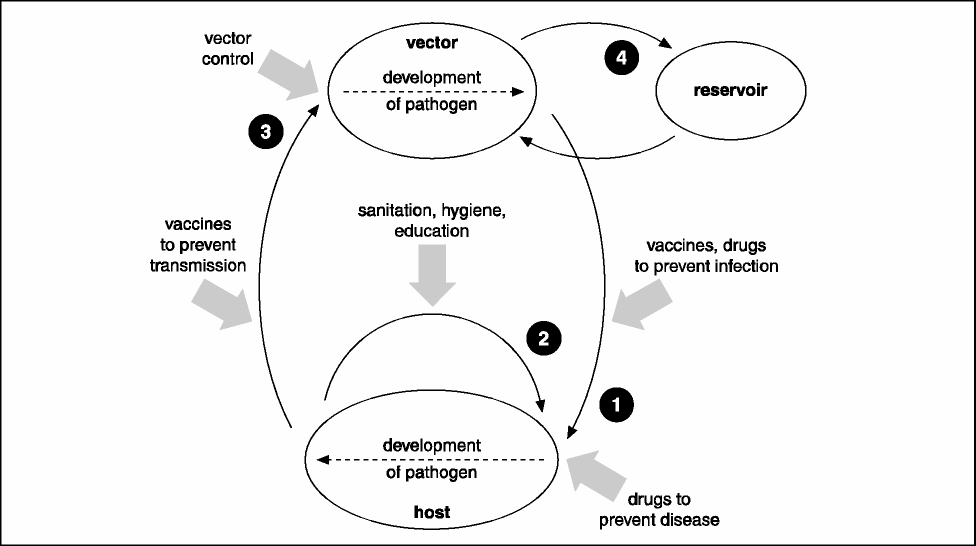
Infectious diseases can be pre vented at a variety
food and beverages contaminated by contact
of points, depending on the infectious cycle for
with a disease reservoir is another example
the particular disease (Figure 4). Basic research,
of disease transmission by indirect contact.
such as that sponsored by NIH, reveals the
The fecal-oral route of transmission, in which
specific infectious cycle and details regarding
sewage-contaminated water is used for drinking,
the activities of the pathogen that cause disease
Figure 4. The black arrows illustrate a generalized infectious cycle; the shaded arrows indicate points where infectious diseases can be prevented. (1) A host is infected by the reservoir or a vector for the pathogen. This individual may infect (2) other hosts in a population or (3) new vectors. (4) The pathogen may also cycle between the vector and a reservoir.
23
Understanding Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
(for example, the particular cells, if any, that
membranes that trap airborne particles and
are attacked and the toxins produced by the
prevent most of them from reaching the lungs.
pathogen that damage host tissues).
Other anatomical barriers are the skull and
vertebral column, which protect the central
Understanding the infectious cycle is critical to
nervous system—few pathogens are able
identifying accessible targets for control strategies
to penetrate bone. The skin is also a major
(Figure 4). For example, direct person-to-person
anatomical barrier to microorganisms. The
transmission may be inhibited by proper hygiene
surface layer of dead, hardened cells is relatively
and sanitary conditions as well as by education
dry, and skin secretions make the surface
about disease prevention. Vector-borne diseases
somewhat acidic. When sweat evaporates, salt is
may be prevented by control measures that
left behind on the skin. All of these conditions
either kill the vector or prevent its contact with
(low moisture, low pH, and high salinity)
humans. Infection by a pathogen or development
prevent most microorganisms from growing
of a pathogen within a host may be prevented
and multiplying on the skin. The major medical
by vaccination. Finally, drugs may be used to
challenge in treating burn patients is preventing
prevent infection or suppress the disease process.
and treating infections that result because of
the absence of skin that ordinarily would
The tools, including drugs, vaccines, and vector-
prevent invasion of microorganisms.
control methods, are already available to deal
with some diseases. For other diseases, the
Natural openings are also protected by a variety
methods for control are inadequate, undeveloped,
of physiological deterrents. For example, tears
or nonexistent. Scientists are trying to develop
continuously flush debris from the eyes. Vaginal
the new tools needed to banish these scourges of
secretions are acidic, a hostile environment that
humankind. This requires basic research into the
discourages the growth of many pathogens. The
life processes of the pathogen and its interaction
eye, mouth, and nasal openings are protected
with the host in order to identify points within
by tears, saliva, or nasal secretions that contain
the life cycle where the pathogen is vulnerable
lysozyme, an enzyme that breaks down bacterial
to intervention, translational research to develop
cell walls. Blood, sweat, and some tissue fluids
new tools (such as vaccines or antimicrobial
contain lysozyme as well.
drugs), and clinical research to test the safety
and efficacy of these new tools.
In addition to lysozyme, the blood has many
elements that defend the body from disease-
Host Defenses Against
causing organisms. The white blood cells include
Infectious Diseases
several types of phagocytic cells that detect,
The human body has several general mechanisms
track, engulf, and kill invading bacteria and
for preventing infectious diseases. Some of these
viruses, as well as infected host cells and other
mechanisms are referred to as nonspecific defenses
debris. These phagocytic cells are part of the
because they operate against a wide range of
nonspecific immune system. Blood plasma also
pathogens. Other mechanisms are referred to as
includes clotting factors that initiate a clot at the
specific defenses because they target particular
injury site, preventing pathogens from invading
pathogens and pathogen-infected cells.
the body further. Finally, the complement
proteins in the blood participate in a cascade of
Nonspecific mechanisms. Nonspecific
molecular events that result in inflammation, the
mechanisms are the body’s primary defense
release of molecules that stimulate phagocytic
against disease. These mechanisms include
cells, and the formation of a complex of proteins
anatomical barriers to invading pathogens,
that binds to the surface of bacterial or infected
physiological deterrents to pathogens, and the
host cells and lyses those cells.
presence of normal flora. An example of an
anatomical barrier is the nasal opening to the
The inflammatory response is another nonspecific
respiratory system. This natural opening is a
defense mechanism that helps prevent infectious
long, convoluted passage covered by mucous
agents from spreading in the body. Inflammation
24
involves swelling, reddening, elevated temperature,
as the proteins on the surface of pathogens, that
and pain. Unfortunately, inflammation itself
elicit an immune response. This display helps
frequently causes tissue damage and, in severe
the macrophages stimulate specific helper T-cells
cases, even death.
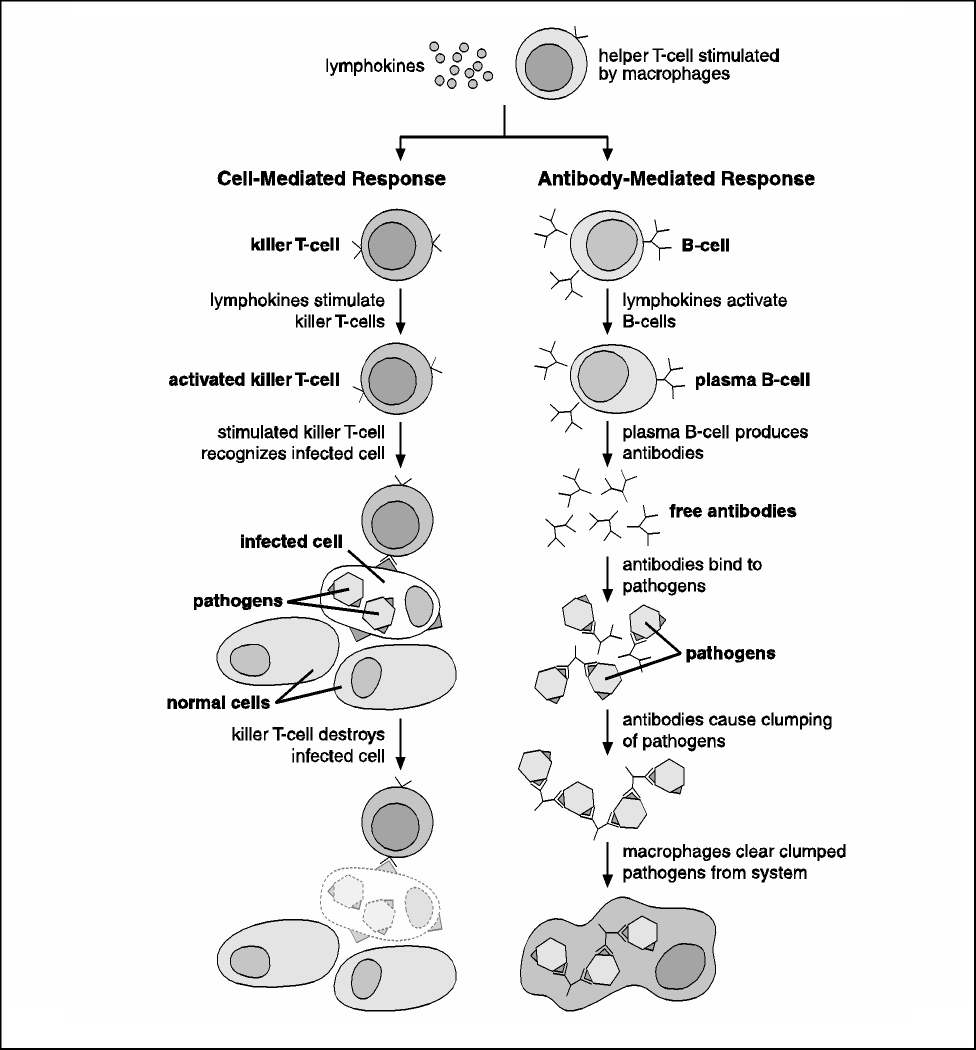
to release signal molecules called lymphokines.
The lymphokines, in turn, stimulate the cell-
The protective role of the “normal flora” of
mediated and antibody-mediated responses.
microorganisms present on and in the body should
not be overlooked. These organisms survive and
The cell-mediated response occurs when the
grow on the skin and in the mouth, gastrointestinal
lymphokines released from the helper T-cells
tract, and other areas of the body but do not cause
stimulate other cell types to participate in the
disease because their growth is kept under control
immune response. Lymphokine-stimulated killer
by the host’s defense mechanisms and by the
T-cells attach to the pathogen-infected cells and
presence of other microorganisms. These organisms
destroy them, whereas lymphokine-activated
protect the host by successfully competing with
phagocytic cells produce more toxic molecules
disease-causing organisms, preventing the latter
that can kill the pathogen directly.
from invading host tissues. When the growth of
the normal flora is suppressed (for example, due
The antibody-mediated response occurs when the
to antibiotic treatment), other “opportunistic”
lymphokines activate specific B-cells to produce
agents that normally do not grow in or on the
antibodies (proteins that specifically recognize
body may be able to infect and cause disease.
and bind to antigens). These antibodies attach to
antigens on the surface of the pathogens and signal
Specific mechanisms of host resistance. When
attack by phagocytic cells and the complement
these nonspecific mechanisms fail, the body
system. Other B-cells go on to become memory
initiates a second, specific line of defense. This
B-cells, which respond quickly by producing
specific immune response enables the body to
more antibodies upon subsequent infection.
target particular pathogens and pathogen-infected
cells for destruction. It depends on specialized
Immunity. When a host encounters an antigen
white blood cells called lymphocytes and includes
that triggers a specific immune response for the
T-cells (produced from lymphocytes that matured
second or later time, the memory lymphocytes
in the thymus gland) and B-cells (produced from
recognize it and quickly begin growing and
lymphocytes that matured in the bone marrow).
dividing, as well as producing high concentrations
of lymphokines and antibodies. Because memory
The two complementary components of the
cells are present, this response happens much
specific immune response are the cell-mediated
more quickly than in the initial encounter with
response and the antibody-mediated response
the antigen. This rapid response explains why
(Figure 5). The cell-mediated response involves
hosts are immune to developing many diseases
T-cells and is responsible for directly destroying
a second time: The immune response occurs so
body cells that are infected with a virus or have
quickly in a second encounter with the pathogen
become cancerous, or for activating other
that the pathogen does not have enough time to
immune cells to be more efficient microbe
reproduce to concentrations that result in disease
killers. The antibody-mediated response involves
before the host’s body has destroyed it. The
both T-cells and B-cells and is critical for the
memory response also explains the effectiveness
destruction of invading pathogens as well as
of vaccination for preventing even the first
the elimination of toxins.
occurrence of many diseases.
Both the cell-mediated and antibody-mediated
Vaccination. A vaccine is either a killed or
responses are initiated after a particular type
weakened (attenuated) strain of a particular
of phagocytic cell, a macrophage, engulfs a
pathogen, or a solution containing critical
pathogen. Macrophages digest the pathogen and
antigens from the pathogen. The body’s immune
then display antigens from the pathogen on their
system will respond to these vaccines as if they
surface. Antigens are specific molecules, such
contain the actual pathogen, even though the
25
Understanding Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Figure 5. This diagram provides an overview of specific immunity.
vaccine is not capable of causing the disease.
New types of vaccines, the DNA vaccines, are in
As a result of the specific immune response,
early-stage trials. These vaccines contain genes
memory lymphocytes will be present that respond
that encode proteins from pathogens. When
rapidly when the actual pathogen is encountered.
these genes are inserted into host cells and are
The resulting rapid activation of immune cells
expressed in the form of pathogen proteins, an
prevents disease.
immune reaction may result.
26
The ultimate effectiveness of vaccination—
include settling, filtration, and chlorination. The
eradication of the infectious agent—has been
water for homes that use well water or springs
achieved only for smallpox. The World Health
is usually safe if guidelines about distance from
Organization has identified the polio and measles
sewage disposal facilities are followed; however,
viruses among the next targets for global eradication.
this water should be checked periodically. When
breakdowns in a purification system occur, or
For a variety of reasons, many diseases are
when a system is overwhelmed (for example, due
not easily prevented by vaccination. Antibody
to unusual flooding), drinking water may not be
response is generally the simplest to induce
safe and should be boiled or treated with chlorine
by vaccination, but some pathogens have ways
before it is ingested.
to evade the immune response. Intracellular
pathogens (such as viruses and some bacterial
Because gastrointestinal pathogens typically
and protozoan pathogens) are not directly
leave the body in the feces, public water must
affected by antibodies because antibodies cannot
be guarded against contamination from sewage.
pass inside cells. Moreover, during the disease
Municipal water is usually tested for the
process, some pathogens acquire an external
presence of coliform organisms (nonpathogenic
coat composed of host-derived material while
microorganisms that are part of the normal
others disguise themselves by making molecules
flora of the gastrointestinal tract) as indicators
that resemble host molecules. Thus, the host’s
of sewage contamination. This procedure is
immune system does not identify them as foreign
necessary because when the water contains
invaders. Still other pathogens mutate quickly,
pathogens and is potentially dangerous, the
producing variants of their antigens that are not
pathogenic organisms are usually present in such
recognized by the host’s immune system, even
small numbers that they are hard to detect.
though the host survived a previous encounter
with that pathogen. Cold and influenza viruses
Sewage treatment and disposal. Sewage includes
are examples of rapidly mutating pathogens.
wash water, water from toilets, and storm run-
Scientists are working to improve vaccines
off. These fluids may carry the pathogens for
against these pathogens.
many waterborne diseases, including giardiasis
and hepatitis A. To ensure public safety, the
Public Health Measures to Prevent
U.S. government (and the governments of other
Infectious Diseases
developed countries) requires that sewage be
Developed countries have regulations that
treated to eliminate pathogens. The minimal
help protect the general public from infectious
acceptable level of treatment involves collection
diseases. Public health measures typically involve
and sedimentation of sewage waters, separating
eliminating the pathogen from its reservoir or
solid matter (sludge) from the liquid (effluent)
from its route of transmission. Those measures
portion of sewage. The effluent is chlorinated to
include ensuring a safe water supply, effectively
kill pathogens before it is released to rivers or
managing sewage treatment and disposal,
lakes. The sludge is burned or dumped.
and initiating food-safety, animal-control, and
vaccination programs.
More advanced methods of treatment use a
secondary treatment following this primary
Safe water. Many pathogens that cause
treatment. The effluent is transferred to tanks
gastrointestinal diseases (for example, those
containing a population of microorganisms that
that cause hepatitis A and typhoid fever) are
decompose more than 90 percent of the organic
transmitted via water. Travelers to developing
wastes and eliminate pathogens by competition
countries are frequently advised to be immunized
(this is another example of the important role
against these diseases. This is generally
of microorganisms in preventing disease). The
unnecessary in the United States and other
resulting effluent is chlorinated before it is released
developed countries because the water used for
to the environment. Some sewage-treatment plants
washing, drinking, and preparing food is purified
include a tertiary treatment that involves additional
before it goes into homes. Purification methods
chemicals that also eliminate pathogens.
27
Understanding Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Emerging and Re-emerging Infectious Diseases
Food-safety programs. The United States
some states allow certain exemptions, including
has many standards, inspection plans, and
exemptions based on religious beliefs. The value
regulations about food preparation, handling, and
of immunization for an individual’s health is
distribution. Meatpacking facilities are inspected
obvious; however, it is also important for public
regularly so that diseased animals can be detected
health. If a certain proportion of a population
and eliminated, standards for processes such as
(called the threshold proportion) is immune to
meat cutting and refrigeration are observed, and
a disease, the pathogen that causes that disease
residues from pesticides and antibiotics as well
will be unable to reproduce itself at a high
as contamination by bacteria and other parasites
enough level to maintain itself in the population.
are detected. Restaurants and supermarkets
This is because once the infected host recovers
are similarly inspected. Milk is pasteurized
or dies, there will not be enough new, susceptible
and dated for sale and is analyzed periodically
hosts for the pathogen to infect. Eventually, the
for contamination. Industry standards for
pathogen cannot spread any further and could
canning and preserving foods are maintained
be eliminated from the population. Even if
through periodic quality-control






