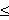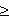8. CONCLUSION
It is an interesting option to extend this study from different perspectives : green information system, computation of MPPT based on AI, construction of quantitative models foe self healing mechanism and real-time fault diagnostics. A solar computing system must ensure real-time secure monitoring and sense-and-respond modeling; the system should be able to tune itself automatically to an optimal state adaptively. It should be able to anticipate various types of threats automatically that could disturb the stability of the system. Another important task is to isolate the healthy part from the faulty one. A smart power grid is vulnerable to both natural disasters and intentional attacks, physical and cyber challenges and threats of deception. The size and complexity of the grid structure and related cost of erection, testing, commissioning and maintenance are the major constraints to protect the entire infrastructure physically. There are also threats of act of terrorism on the disruption of smart grid and related adverse effects on national security, economy and the quality of life of the common people. Energy security demands fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of the existing power grids globally.
Intelligent business and technical analysis of IIOT, ICS and SCADA requires the availability of critical up-to-data, analytical models and tools for rational, fair and correct evaluation of technology innovation. This study can be extended in various ways. It is interesting to extend the scope of the aforesaid system in various emerging applications such as banking and financial services, defense and e- governance. ICS & SCADA networks are potentially vulnerable to intrusion and various types of malicious cyber attacks which may affect the safety of common people and the performance of critical infrastructure seriously and may cause huge financial loss. It is expected to be a resilient system. This work finds a set of interesting research agenda for future works: how to develop intelligent threat analytics and secure verification algorithms from the perspectives of method, target, identity and protocol to ensure confidentiality, authentication, integrity, availability, accountability and access control of ICS and SCADA infrastructure? how to quantify various parameters of security intelligence? Is it possible to develop automated verification and model checking algorithms for ICS and SCADA? We need a new broad outlook, imagination and dreams to solve a complex problem through a set of simple mechanisms.
The expert panel are highlighting some common SMC tools, it is an interesting option to explore how to construct these tools in the setting of Quantum Computing?
Oblivious transfer: Oblivious transfer (OT) is a bi-party protocol wherein a receiver learns some information regarding the input of the sender such that the sender does not know what the receiver has learnt. The notion of oblivious transfer has several versions. Rabin introduced the concept of oblivious transfer. In the original OT problem, the receiver learns the secret of the sender with probability ½. 1-out-of-2 oblivious transfer (OT12) is a protocol by which a sender (S) transfers ignorantly to a receiver (R) one out of two secret messages (Even, Goldreich and Lempel, 1985). 1-out-of-n oblivious transfer is a protocol between two parties. Here, Alice holds n inputs in a particular sequence which is known only to Bob.. At the end of the protocol, Bob learns only 1 out of n inputs and Alice will not know which input Bob has learnt (Naor and Pinkas, 1999). k-out-of-n oblivious transfer protocol is an extended version of 1-out-of-n oblivious transfer where 1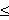 k
k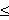 n-1. Distributed oblivious transfer protocol distributes the task of Alice between several servers and each server holds partial information about the secret ( Naor and Pinkas, 2000). The receiver has to contact t (t
n-1. Distributed oblivious transfer protocol distributes the task of Alice between several servers and each server holds partial information about the secret ( Naor and Pinkas, 2000). The receiver has to contact t (t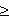 1) or more servers to get the secret otherwise it cannot get any information about the secret. Security is ensured as long as a limited number of servers collude. Oblivious polynomial evaluation is a protocol involving two parties, Alice holding input a polynomial P and Bob with input x. At the end of the protocol, Bob learns P(x) but Alice learns nothing about x. Naor and Pinkas (1999) studied an oblivious evaluation of polynomial problem based on oblivious transfer protocol. Oblivious transfer is a fundamental primitive for cryptography and secure distributed computation and has many applications.
1) or more servers to get the secret otherwise it cannot get any information about the secret. Security is ensured as long as a limited number of servers collude. Oblivious polynomial evaluation is a protocol involving two parties, Alice holding input a polynomial P and Bob with input x. At the end of the protocol, Bob learns P(x) but Alice learns nothing about x. Naor and Pinkas (1999) studied an oblivious evaluation of polynomial problem based on oblivious transfer protocol. Oblivious transfer is a fundamental primitive for cryptography and secure distributed computation and has many applications.
Secure function evaluation: Alice with an input x and Bob with an input y want to evaluate a function z = f(x,y) based on their joint inputs in such a way that does not allow any party to gain more information than that is implied by its inputs and the function value. Alice and Bob can achieve this through a protocol known as secure function evaluation. In the field of secure function evaluation, f is represented in various ways - garbled circuit construction), combinatorial circuit, algebraic, as a product of matrices over a large field; low degree polynomial and randomizing polynomials.
Mixnet : A mixnet consists of multiple independent mix-servers and it enables a group of senders to send their messages anonymously. Chaum (1988) introduced the concept of mixnet. Later, several researchers proposed mixnet protocols for the shuffling of encrypted messages. The concept of mixnet has been widely applied to design efficient electronic voting schemes. In this case, each voter sends his encrypted ballot to a mixnet. The Mixnet shuffles the posted ballots such that the voter-vote relationship is lost. After the mixing process, multiple tally servers jointly decrypt the encrypted ballot and count the votes. Mixnet can be classified into verifiable mixnet and optimistic mixnet on the basis of correctness proof. Each server of verifiable mixnet provides the proof that its shuffling is correct. On the other side, optimistic mixnet does not provide the verification of correct shuffling by each server. The correctness of the shuffling of the whole mixnet is verified after it generates the output.
Private comparison : Yao’s millionaire problem is to find out who is richer between two parties such that no information about one party’s value is revealed to the other party. Yao first proposed a protocol for this problem without using any untrusted third party. The cost of the protocol was exponential in both time and space. Later, scrambled circuits has been used to solve this problem at linear cost of computation and communication. Cachin (1999) suggested an efficient solution using an oblivious third party. Fishchlin (2001) used the Goldwasser-Micali (GM) encryption scheme to construct a two round non-interactive crypto-computing GT (greater than) protocol. Two inputs can be compared by verifying the most significant bit in which they are different. Similar bits do not affect the result and the effect of unequal low order bits is overshadowed by the high order bits. Based on this principle, Ioannidis and Grama (2003) proposed a private comparison protocol using oblivious transfer scheme. Schoenmaker and Tuyls (2004) used threshold homomorphic encryption scheme to solve private comparison problem. Blake and Kolesnikov (2004) used the concepts of Q-conditional oblivious transfer and the additive homomorphic Paillier cryptosystem to construct a two round private comparison protocol. The computation cost is O(nlogN) where n is the length of the inputs and N is the size of the plaintext domain of Paillier scheme.
In this session, the panel have analyzed the complexity of emerging technology of secure multi-party quantum computing by reviewing various related works [1-15] - what are the fundamental concepts of quantum computation and quantum information? what are the scopes of application of SMQC? How to develop these concepts? how to develop quantum errors correctling codes and fault tolerant quantum computation? how to develop cryptographic protocols, private and public key cryptosystems in the setting of SMQC? Wht is the future of SMQC? What can quantum computation and quantum information offer to science, technology and humanity? What are the benefits of SMQC upon omputer science, information theory and Physics? What are the key open problems of quantum computation and quantum information? SMQC is the basic building block to think physically about computation and it yields many new exciting capabilities for information processing and communication. Secure multi-party quantum computation offer hard challenges in terms of computation and communication complexity.
This session shows the application of cryptographically secure protocols for kernelized Support Vector Machines of secure adaptive filter.However, there are still many open problems in private SVM classification, learning and secure adaptive filters. An interesting question is how to compute and securely hide the convergence speed of the private SVM algorithms? Are there any iterative private linear classification methods that need no circuit evaluation. Another relevant issue is private computation of encrypted kernel matrices for structured data. A protocol preserves privacy if no agent learns anything more than its output; the only information that should be disclosed about other agent’s inputs is what can be derived from the output itself. Secure multi-party computation preserves privacy of data in different ways; is it possible to apply SMC protocols for secure adaptive filter? What are the algorithms? is the cost of computation and communication high in secure multi-party computation of an adaptive filter? Privacy is one of the primary concerns of secure adaptive filter; is it possible to address the issue utilizing the concept of cryptography and secure multiparty computation? The fundamental objectives of cryptography are to provide confidentiality, data integrity, authentication and non-repudiation. Cryptography ensures privacy and secrecy of information through encryption and decryption methods. The challenge is how to apply existing encryption and decryption algorithms in secure adaptive filter : is it possible to perform quantitative operations of secure adaptive filter on encrypted data? How? Is it possible to apply digital signature for secure adaptive filter? how to apply existing digital signature algorithms in secure adaptive filter : is it possible to perform quantitative operations of secure adaptive filter on digitally signed data? How? Is it possible to apply signcryption for secure adaptive filter? how to apply existing signcryption and unsigncryption algorithms for secure adaptive filter : is it possible to perform private search on signcrypted data? How?
The central message of this summit is that the success of technology innovation projects depends on several factors: strength, weakness, opportunities, threats, technology life-cycle, understanding the needs of consumers, competitive environment, blind spots and the ability to recognize and align the partners associated with the value chain and innovation ecosystem. Deep analytics is essential to coordinate, integrate and synchronize ‘7-S’ elements: scope, system, structure, staff-resources, skill-style-support, security and strategy. Even the most brilliant innovation cannot succeed when its value creation depends on innovation of other technologies. This book evaluates a set of emerging technologies for humanity; most of these technology innovations are at emergence stage, some others are at growth stage. Hopefully, deep analytics should be able to accelerate the pace of these emerging technological innovations. Let us discuss the limitations and future scope of this summit. In fact, the aforesaid content is the summary of the discussions during various sessions of the summit and are focused on emerging technologies associated with electrical and electronics engineering, information and communication technologies and computer science. There are other various branches of science and technology such as Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Earth science, Geology, mechanical, chemical, petrochemicals, oil and gas, pharmacy, biotechnology, genetics, metallurgical, civil, structural, construction, production and power plant engineering. It is essential to have depth and breadth of knowledge to explore emerging technologies in those branches of engineering. Secondly, deep analytics demand the support of quality technical and business data and efficient quantitative tools and techniques to evaluate the potential of a technology, to perform technology life-cycle analysis, technology diffusion, adoption, infusion and innovation, dominant design, blind spots and spillover effects. It is also essential to evaluate these emerging technologies deeply from the perspective of numerical, statistical, quantitative and qualitative analysis based on up-to-date data. In fact, there is no end of this intelligent deep analysis. There is no end of the debate on the strength, weakness, threats and opportunities of emerging technologies and comparison with existing technologies. Let us try to save the world..…
FURTHER READING
-
- Armburst, M. et al. (2010). A view of cloud computing, Communications of the ACM, 53(4), 50-58.
- Buyya, R., Yeo, C.S., Venugopal, S., Broberg,J. and Brandic, I. (2009). Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms: Vision, hype and reality for delivering computing as the 5th utility. Future generation computer systems.
- Chakraborty, S. (2007). A study of several privacy-preserving multi-party negotiation problems with applications to supply chain management. Fellow programme dissertation, Indian Institute of Management Calcutta.
- Forouzan, B.A. (2007). Cryptography & network security. McGraw Hill.
- Furht,B. and Escalante, A. (2010). Handbook of Cloud Computing. Springer.
- Goldreich, O. (2004). Foundations of Cryptography, Basic Applications. Volume 2. Cambridge University Press.
- Reports of Gartner and Forrester; 2017,2018,2019.
- Beloglazov, A., Buyya, R., Lee, Y.C and Zomaya, A. (2011). A taxonomy and survey of energy efficient data centers and cloud computing systems. Advances in computers, volume 82.
- Wang (2012). "Enterprise cloud service architectures". Information Technology and Management. 13 (4): 445–454. doi:10.1007/s10799-012-0139- 4.
- "What is Cloud Computing?". Amazon Web Services. 2013-03-19. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- Ted Simpson, Jason Novak, Hands on Virtual Computing, 2017, ISBN 1337515744, p. 451
- Gruman, Galen (2008-04-07). "What cloud computing really means". InfoWorld.
- Kumar, Guddu (9 September 2019). "A Review on Data Protection of Cloud Computing Security, Benefits, Risks and Suggestions" (PDF). United International Journal for Research & Technology. 1 (2): 26. Retrieved 9 September2019.
- Antonio Regalado (31 October 2011). "Who Coined 'Cloud Computing'?". Technology Review. MIT.
- Griffin, Ry'mone (2018-11-20). Internet Governance. Scientific e- Resources. ISBN 978-1-83947-395-1.
- "Distributed Application Architecture". Sun Microsystem.
- Bruneo, Dario; Distefano, Salvatore; Longo, Francesco; Puliafito, Antonio; Scarpa, Marco (2013). "Workload-Based Software Rejuvenation in Cloud Systems". IEEE Transactions on Computers. 62 (6): 1072–1085. doi:10.1109/TC.2013.30.
- Kuperberg, Michael; Herbst, Nikolas; Kistowski, Joakim Von; Reussner, Ralf (2011). "Defining and Measuring Cloud Elasticity". KIT Software Quality Departement. doi:10.5445/IR/1000023476.
- Marston, Sean; Li, Zhi; Bandyopadhyay, Subhajyoti; Zhang, Juheng; Ghalsasi, Anand (2011-04-01). "Cloud computing – The business perspective". Decision Support Systems. 51(1): 176–189. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2010.12.006.
- Mills, Elinor (2009-01-27). "Cloud computing security forecast: Clear skies". CNET News.
- Boniface, M.; et al. (2010). Platform-as-a-Service Architecture for Real-Time Quality of Service Management in Clouds. 5th International Conference on Internet and Web Applications and Services (ICIW). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE. pp. 155–160. doi:10.1109/ICIW.2010.91.
- Butler, Brandon (2017-10-17). "What is hybrid cloud computing? The benefits of mixing private and public cloud services". Network World.
- "Business Intelligence Takes to Cloud for Small Businesses". CIO.com. 2014- 06-04.
- Haghighat, Mohammad; Zonouz, Saman; Abdel-Mottaleb, Mohamed (2015). "CloudID: Trustworthy cloud-based and cross-enterprise biometric identification". Expert Systems with Applications. 42 (21): 7905–7916. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2015.06.025.
- Ray, Neville (June 18, 2018). "FCC testimony Neville Ray". FCC.gov
- "Preparing the ground for IMT-2020". www.3gpp.org. Archived from the original on April 14, 2019.
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, Shu; Mayzus, R.; Zhao, Hang; Azar, Y.; Wang, K.; Wong, G.N.; Schulz, J.K.; Samimi, M. (January 1, 2013). "Millimeter Wave Mobile Communications for 5G Cellular: It Will Work!". IEEE Access. 1: 335–349. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2013.2260813. ISSN 2169-3536.
- Nordrum, Amy; Clark, Kristen (January 27, 2017). "Everything you need to know about 5G". IEEE Spectrum magazine. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers. Archived from the original on January 20, 2019.
- Hoffman, Chris (January 7, 2019). "What is 5G, and how fast will it be?". How-To Geek website. How-To Geek LLC. Archived from the original on January 24, 2019.
- Segan, Sascha (December 14, 2018). "What is 5G?". PC Magazine online. Ziff-Davis. Archived from the original on January 23, 2019.
- Shatrughan Singh (March 16, 2018). "Eight Reasons Why 5G Is Better Than 4G". Altran. Archived from the original on May 25, 2019.
- G.Chalkiadakis, V. Robu, R.Kota, A. Rogers and N.R. Jennings. 2011. Cooperatives of distributed energy resources for efficient virtual power plants. In Proc. of 10th Intl. Conf. on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, May, 787–794.
- S.Chowdhury, S. Chowdhury and P. Crossley. 2009. Microgrids and Active Distribution Networks. Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET).
- E. Davidson, S. McArthur, C.Yuen and M.A. Larsson. 2008. Towards the delivery of smarter distribution networks through the application of multiagent systems technology. IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, 1– 6.
- M.Deindl, C. Block, R. Vahidov and D.Neumann. 2008. Load shifting agents for automated demand side management in micro energy grids. In Proc. of 2nd IIEEE Intl. Conf. on Self-Adaptive and Self-Organizing Systems, 487– 488.
- A. Dimeas and N.Hatziargyriou. 2007. Agent based control of virtual power plants. In Proc. of the Intl. Conf. on Intelligent Systems Applications to Power Systems, 1– 6.
- J. McDonald. 2008. Adaptive intelligent power systems: Active distribution networks. Energy Policy 36, 12, Foresight Sustainable Energy Management and the Built Environment Project, 4346–4351.
- S. Ramchurn, P. Vytelingum, A. Rogers and N.R. Jennings. 2011. Agent- based homeostatic control for green energy in the smart grid. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2, May.
- S.D. Ramchurn, P. Vytelingum, A. Rogers and N.R. Jennings. 2011. Agent- based control for decentralized demand side management in the smart grid. In Proc. of the 10th Intl. Conf. on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. May, 5–12.
- P. Ribeiro, B. Johnson, M.Crow, A. Arsoy and Y. Liu. 2001. Energy storage systems for advanced power applications. In Proc. of IEEE 89, 12, 1744 – 1756.
- G. Strbac. 2008. Demand side management: Benefits and challenges. Energy Policy 36, 12, 4419–4426.
- V. Sundramoorthy, G.Cooper, N. Linge and Q. Liu. 2011. Domesticating energy-monitoring systems: Challenges and design concerns. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 10, 20–27.
- P. Vovos, A. Kiprakis, A. Wallace, A. and G. Harrison. 2007. Centralized and distributed voltage control: Impact on distributed generation penetration. Power Systems, IEEE Transactions, 22, 1, 476– 483.
- P.Vytelingum, T.D.Voice, S.D., Ramchurn, A. Rogers and N.R.Jennings. 2010. Agent-based micro-storage management for the smart grid. In Proc. of 9th Intl. Conf. on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, May, 39–46.
- EU SmartGrid Technology Platform. Vision and strategy for Europe’s electricity networks of the future. Tech. Report, European Union, 2006.
- J. Froehlich, L. Findlater and J. Landay. 2010. The design of eco-feedback technology. In Proc. of 28th Intl. Conf. on Human Factors in Computing Systems. ACM, NY, 1999–2008.
- E.Rich and K. Night. 1991. Artificial intelligence. 2nd edition. Mcgraw-Hill, New York.
- H. Eriksson 1996. Expert system in knowledge servers. IEEE Expert.
- Y. Afek and S. Dolev. 2002. Local Stabilizer. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, special issue on self-stabilizing distributed systems, Vol. 62, No. 5, pp. 745-765, May.
- E. Anceaume, X. Defago, X., M. Gradinariu and M.Roy. 2005. Towards a theory of self-organization. 9th International Conference on Principels of Distributed Systems, OPODIS, pp. 146-156.
- M.Chandy and L.Lamport. 1985. Distributed snapshots: determining global states of distributed systems. ACM Transactions on Computing Systems, 3(1):63-75.
- E.W. Dijkstra. 1974. Self-stabilizing systems in spite of distributed control. Communications of the ACM, 17(11):643-644.
- S. Dolev and T.Herman. 1995. Super Stabilizing Protocols for Dynamic Distributed Systems. Proc. of the 2nd Workshop on Self-Stabilizing Systems, May.
- S.Ghosh, A.Gupta, T.Herman and S. Pemmaraju. 1996. Fault-Containing Self-Stabilizing Algorithms. PODC 1996, pages 45–54.
- G. Varghese. 2000. Self-stabilization by counter flushing. SIAM Journal on Computing, 30(2):486-510.
- H. Zhang and A. Arora. 2002. GS3: Scalable Self-configuration and Self- healing in Wireless Networks. Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing, pages 58-67.
- Clemente. 2009. The security vulnerabilities of smart grid. J. Energy Security, June.
- G. N. Ericsson. 2009. Information security for electric power utilities (EPUs)- CIGRE developments on frameworks, risk assessment and technology. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 1174–1181, July.
- P. McDaniel and S. McLaughlin. 2009. Security and privacy challenges in the smart grid. IEEE Security Privacy, vol. 7, no. 3, pp.75–77, May/June.
- NIST. 2010. Guidelines for smart grid cyber security. The Smart Grid Interoperability Panel - Cyber Security Working Group, NISTIR 7628, Gaithersburg, MD, August.
- S. M. Amin. 2010. Securing the electricity grid. Bridge, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 13– 20, Spring.
- S. M. Amin. 2005. Energy infrastructure defense systems. Proc. IEEE, vol. 93, no. 5, pp. 861–875, May.
- S. M. Amin. 2004. Balancing market priorities with security issues: Interconnected system operations and control under the restructured electricity enterprise. IEEE Power Energy Mag., vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 30–38, Jul./Aug.
- J.Brocke, R. T. Watson, C. Dwyer, S. Elliot, and N. Melville. 2013. Green Information Systems: Directives for the IS Discipline. Communications of the Association for Information Systems 33 (1): 509--520.
- C. A. Santos, S. C. Romero, C. P. Molina, and M. Castro-Gil. 2012. Profitability Analysis of Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Facilities for Household Electricity Self-Sufficiency. Energy Policy 51 (December): 749–64.
- P. Cramton. 2017. Electricity Market Design. Oxford Review of Economic Policy 33 (4): 589–612.
- G. Christoph, H. Jacobsen, V. Razo, C. Doblander, J. Rivera, J. Ilg, C. Flath. 2014. Energy Informatics. Business & Information Systems Engineering 6 (1): 25–31.
- C.Loock, T. Staake and F. Thiesse. 2013. Motivating Energy-Efficient Behavior with Green IS: An Investigation of Goal Setting and the Role of Defaults. MIS Q. 37 (4): 1313–1332.
- N.P.Melville. 2010. Information Systems Innovation for Environmental Sustainability.MIS Quarterly, 34 (1): 1--21.
- M. Paschmann and S. Paulus. 2017. The Impact of Advanced Metering Infrastructure on Residential Electricity Consumption - Evidence from California. Working Paper WP 17/08. University of Cologne.
- P. Markus, W. Ketter, M. Saar-Tsechansky, and J. Collins. 2013. A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Autonomous Decision-Making in Smart Electricity Markets. Machine Learning, 92 (1): 5–39