
Internet selling is on the rise. There are many research studies and statistics that support this statement. A study conducted by the Ipsos Reid market research firm in February 2003 concludes that in the year 1999 only 28% of worldwide Internet users purchased a product or service online, whereas this figure rose to 62% in the year 2002 and about 70% in the year 2005. And these numbers continue to climb. Nielsen/NetRatings supports this finding with its own research.
The Internet is a huge marketplace that has attracted businesses with its potential for big-time revenues. Dizzying success stories of ventures started in a basement that grew to become stock market darlings are constantly celebrated in the media. Small businesses came to the Internet, tentative at first, and then in droves - eager to sell everything from fake jewelry to handcrafted tapestries.
You can sell just about anything from soup to nuts, as long as you have a product that has a market.
2.2 What Businesses Are Succeeding on the Net?
After the settling down of the dot-com bubble, sanity checks have brought realistic expectations to the fore. Initially, a backlash was seen, forecasting the doom of the Internet. Finally, merits have made the Internet gain its rightful place. In breakthroughs that show the promise of ecommerce wasn't all smoke and mirrors, many dotcoms including eBay Inc., Amazon.com Inc., Yahoo! Inc., Expedia Inc., FindWhat.com Inc., E-Trade Group Inc., Google Inc. and others have successfully re-defined the landscape of Wall Street.
There is a growing tendency amongst Internet users to pay for valuable content along with quality products and services offered online. Hundreds of paid content and product-oriented websites have already proven this unmistakable trend. The discerning buyer values her time and is willing to pay for access to quality information and the convenience of purchasing products and services online.
However, not all products can be sold on the Internet. Some products may be better suited for online sales than others; others simply will not work online. According to an Ernst and Young study, the most popular online purchases are computer related products (40%), books (20%), travel (16%), clothing (10%), recorded music (6%), subscriptions (6%), gifts (5%) and investments (4%).
Businesses offering paid services have also prospered enormously. The top three categories (Business Content/Investment, Entertainment/Lifestyles and Personals/Dating) consistently account for 62% of all paid content revenue. One statistic indicates that 85% of all money spent by U.S. Consumers for online content goes to the top 50 sites in most categories.
In terms of “stickiness” of different categories, Business sites – especially finance and investment rank the highest. In other words, users are more likely to spend more time surfing through a business website compared to other categories as illustrated below.
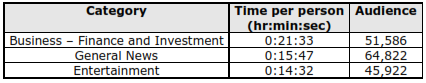
Source: Nielsen/NetRatings
According to the above figures a person spends about 22 minutes on a finance website on average.
Do statistics bore you? Click here to start using a proven Internet money making system that has already been “figured out”.
No thinking… Just follow the 3 steps and launch your e-business today.
2.3 Should you be selling a product or a service?
The Internet is primarily used to communicate, entertain, educate and research. It is thus no wonder that nonperishable, information-intensive products - including computers and software, books, travel, consumer electronics, magazine subscriptions - are the most popular online products at present. Content-rich sites, subscription-based sites to advertiser-supported sites focusing on a wide range of topics, have been sprouting up all over the Internet.
Services such as hotel reservation, air travel and investments have successfully transitioned themselves to the Internet. Unique services such as online driving schools have been prospering too. In fact, many states in the US have already set up online payment sites for Government services. Residents can now get online to pay most of their bills and other expenses including parking tickets to local courts.
However, all kinds of services cannot be run entirely on the Internet. The Internet is less effective when face-to-face selling is needed to close a deal. The Internet can give lots of preliminary information that's useful in setting the scene for the closing. But the actual closing takes place offline - i.e., not on the Internet.
Products can also be marketed and sold successfully on the Internet. The kinds of products and services that sell best on the Internet are those that take advantage of the convenience of the Net.
Remember that convenience is the primary reason consumers flock to the Internet in the first place. People can shop at any hour of the day at most sites. They can avoid crowded stores, irritating sales clerks, and even avoid pickpockets.
Offbeat or unusual products and services often attract online attention and sell strongly. You would generally not try to sell items people can get at the corner store. Thus, few toothbrushes are sold on the Net; the same thing with daily food and beverage purchases. But special cheeses, rare cigars, Turkish plates, long-aged wines, even diamonds, can and do sell well on the Internet.
Most products sold by catalog and mail order also sell well on the Net. However, people tend to buy only those products that can be shipped at a reasonable price. Higher shipping costs diminish the price competitiveness of online products and turns-off a lot of potential buyers. In fact, high shipping costs is the primary factor that discourages some people from buying online more than any other given reason. An Ernst and Young report shows that 53 percent of online shoppers are concerned with shipping costs that are too high, compared to only 19 percent who are concerned with credit card information being stolen.
As an online merchant, you have to work out the advantages as well as disadvantages of selling either products or services online. If you choose to sell a product or service online, you must evaluate your offering to ensure that the total costs of the product or service including shipping are not much higher than what is offered elsewhere.
2.4 Importance of Backend Selling
Considerable effort is required to get customers for your products. You might design stunning web pages, work hard for high search engine rankings (or pay for them), submit classified ads, etc. but still not manage to sell enough to make the kind of profits you desire. This is where the concept of backend sales is useful.
Most marketers are successful because they apply backend selling into their marketing efforts. Backend selling is when you sell other products or services to your existing customers after they have purchased an initial product.
It is always easier to sell products or services to your existing customers because you have developed a relationship with them when you sold your first product or service to them. You will find it less expensive to sell to old customers as compared to selling to new customers.
Your conversion ratio will be dramatically higher with existing customers. In fact, to increase your online profits dramatically, you should continually locate or create new backend products and services to recommend (sell) to your existing customers.
Many businesses sell their front-end products (initial products) at almost zero profit in order to generate backend profits. These businesses do not care even if they lose money on the front-end products or services; they want the backend profits.
How do you make backend sales? There are several ways. When you order a product from a mail-order company, they'll send you a catalog along with your order, or put you on a mailing list and send you new catalogs from time to time. They might also send you a sales letter for another product. This may be related to the first product in some way. Many companies implement such a strategy.
To implement this technique online, you can put the sales pitch for your backend item in the email to the customer that confirms their order. If you have an online catalog, you could include a link to it, or even include a coupon or special offer "for all valued customers".
For a faster response, you should put the backend offer on the "Thank You" page that is generated by a credit-card sale. The customer just bought something from you and has a credit card in his or her hot little hand! Why not ask for another purchase while they are in the mood to buy. In case you do not sell more than one product or service, affiliate programs might come in handy.
Backend selling can also be integrated with “Up-Selling” wherein you introduce more expensive products or services to your existing customers in similar ways as those mentioned above. This will almost instantly raise your sales and profits.
TIP: With the Plug-In Profit Site service, you get an automated backend sales campaign built directly into the website I build for you. Click here to learn all about it and start earning backend sales today.
2.5 Cross-Selling
Another successful strategy similar to the ones discussed above is cross-selling. One of the best examples of cross-selling via the web is on Amazon.com. If you search for a book on the Amazon site, a message will appear on the same page, saying “Customers who bought this book also bought…” and will list half-dozen other books for your consideration. This is an excellent way to cross-sell additional services or content to your members.
You can also direct visitors to other parts of the site to consider products and services that they hadn't previously considered. Successful cross-selling is the result of recognizing a customer need and meeting that need with a useful product or service. Customers benefit from needs-based cross-selling efforts because they receive the services they need and want.
Cross-selling can help your business realize its objectives: providing useful services, retaining customers, attracting new customers, and staying competitive with other websites.
In conclusion, you can offer a range of products and services on the Internet. The key is proper research and a great marketing plan. We’ll be talking about marketing strategies for your product or service in the upcoming chapters. In fact, in the next chapter, we will discuss one of the most important Internet marketing strategies – search engine optimization.





